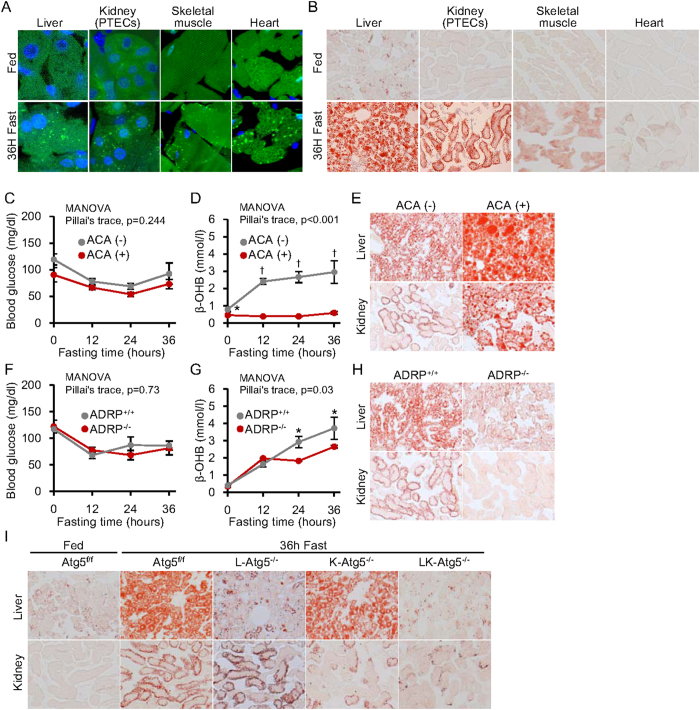
Figure 3. Effect of autophagy-deficiency on starvation-induced lipid droplet formation in liver and kidney.
(A) Starvation-induced autophagy activation was detected in liver, skeletal muscle, heart and kidney proximal tubules of GFP-LC3 transgenic mice as green dotted fluorescence signals. Original magnification: 1000×. (B) Starvation-induced triglyceride accumulation in various tissues of mice, determined by Oil Red O staining. Original magnification: 100×. (C–E) Animal study using L-aminocarnitine (L-ACA) treatment to impair fatty acid utilization in the mitochondria. (C,D) Blood glucose (C) and β-hydroxybutyrate (β-OHB) levels (D) in mice, with and without L-ACA treatment, during 36 h fasting (n = 9 per group). (E) Oil Red O staining to visualise lipid droplets in liver and kidney from mice, with and without L-ACA treatment, after 36 h starvation. Original magnification: 100×. (F–H) Animal study comparing adipose differentiation-related protein knockout (ADRP−/−) to wild type (ADRP + / + ) mice. ADRP is a protein essential to the formation of lipid droplets. (F,G) Blood glucose (F) and β-OHB levels (G) in ADRP−/− and ADRP + / + mice during 36 h fasting (n = 4 per group). (H) Oil Red O stain showing lipid droplets in liver and kidney tissues after 36 h starvation. Original magnification: 100×. (I) Oil Red O stain showing lipid droplets in the autophagy-deficient tissues of L-Atg5−/−, K-Atg5−/− and LK-Atg5−/− mice after 36 h starvation. Original magnification: 100×. Data are means ± SEM. *P < 0.05, †P < 0.01.