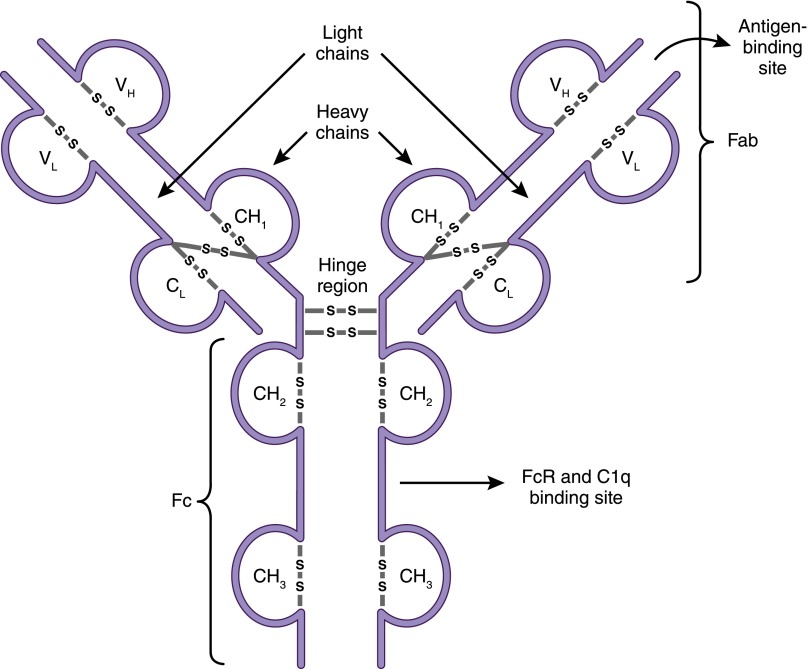
Figure 2.
Antibody structure. Antibodies (immunoglobulins) are composed of two heavy chains (VH and CH) and two light chains (VL and CL). The antigen-binding fragment, Fab, is composed of one variable domain from each heavy and light chain (VH and VL). The variable domains contain the complementarity determining regions (CDRs) with the most sequence variations and determine antibody specificity. The constant domains CH2 and CH3 of the heavy chain make up the crystallizable fragment, Fc, which mediates effector functions through binding to Fc receptors (FcRs) on cells and to complement (C1q).