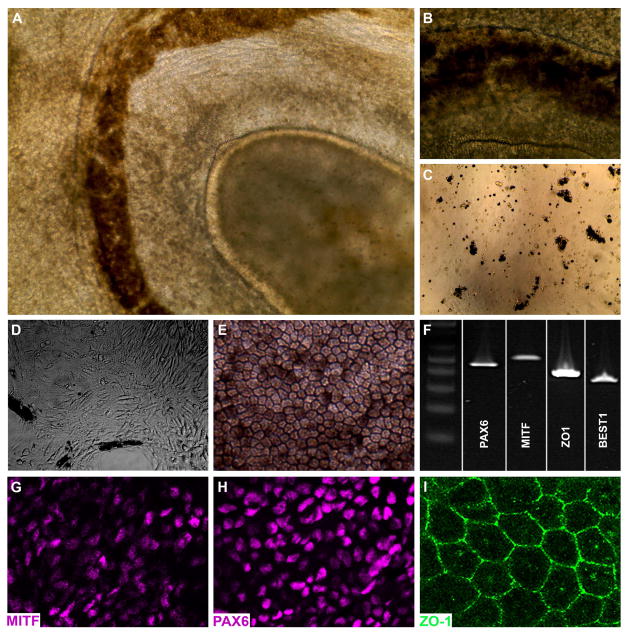
Figure 2. Generation of iPSC-derived RPE cells from a patient with clinically diagnosed LCA.
A–B: iPSC-derived eyecup-like structures generated from a patient with clinically diagnosed LCA (A, low magnification – B, high magnification). C–E: Following isolation, dissociation and subculture (C), pigmented cells adhere to the cell culture surface, spread, lose pigmentation, and assume a fibroblastic morphology (D). By 3 weeks post-plating, a confluent monolayer of RPE cells are present that have taken on the typical cuboidal RPE morphology and regained pigmentation (E). F: RT-PCR analysis using primer pairs targeted against the RPE transcription factors PAX6 and MITF, the tight junction marker ZO1, and the RPE-specific channel BEST1. G–I: Immunocytochemical analysis using antibodies targeted against the RPE transcription factors PAX6 (G) and MITF (H), and the tight junction marker ZO1 (I).