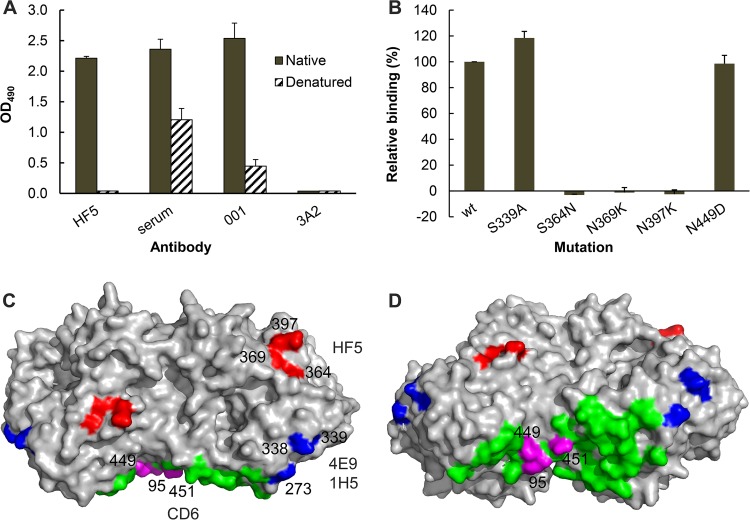
FIG 1.
MAbs HF5, CD6, 4E9, and 1H5 bind different epitopes in the NA of pH1N1 virus. (A) MAb HF5 binds to native but not denatured CA/09-X179A. Data from ELISA show the binding of HF5 to purified whole virus (solid bars) but not CA/09-X179A that has been dissociated and heat denatured (hatched bars). Assay controls are labeled serum (mouse serum against CA/09 virus), 001 (rabbit MAb against CA/09 NA), and 3A2 (MAb specific to the NA of BR/07-like H1N1 virus). Shown are mean OD490 values from two independent assays run in duplicate wells; standard deviations (SDs) are shown with error bars. (B) Binding of MAb HF5 to a panel of mutant CA/09 NAs expressed on 293T cells. The binding was measured by a cell-based ELISA, with the signals being normalized to those obtained with mouse serum against CA/09, which are therefore expressed as relative binding. Shown are the data from two independent assays run in duplicate wells. (C) A model that depicts the residues in an NA dimer (Protein Data Bank accession number 3NSS) that are critical for the binding of MAbs HF5 (red), CD6 (magenta), as well as 4E9 and 1H5 (blue). The remaining 27 residues within the CD6 epitope (Protein Data Bank accession number 4QNP) are highlighted in green. The image was generated with PyMOL software (Delano Scientific). (D) The same model in panel C shown from a different view.