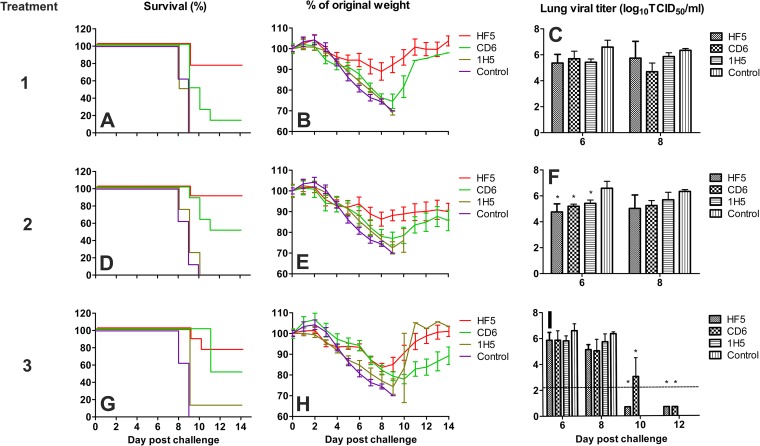
FIG 4.
Therapeutic efficacy of MAbs HF5, CD6, and 1H5 against lethal pH1N1 virus challenge in mice. DBA/2 mice (n = 14 or 20 per group) were infected i.n. with 10 MLD50 of CA/09, followed by injection i.p. with a single dose of each MAb on day 1 p.c., two doses on days 1 and 5 p.c., or three doses (5 mg/kg per dose) on days 1, 3, and 5 p.c (shown as treatments 1, 2, and 3, respectively). MAb 3A2, which is specific to the seasonal H1N1 BR/07 virus, was used as a negative control. Survival (A, D, and G) and weight loss (B, E, and H) (n = 8 per group) were monitored for up to 14 days. Lungs were collected on different days, and viral titers (C, F, and I) were determined by titration in MDCK cells. Titers are expressed as the log10 50% tissue culture infective dose (TCID50) per milliliter; SDs are shown with error bars. The dotted line denotes the detection limit of 2.2 log10 TCID50/ml. A titer of 0.7 log10 TCID50/ml was assigned to samples with titers below the detection limit. The viral titers of the control groups at day 8 p.c. were used for analysis of the titers measured on days 10 and 12 p.c. because none of the mice in the control groups survived at these time points. Significant differences between titers measured in each group and the MAb 3A2-treated control groups are shown (*, P < 0.05).