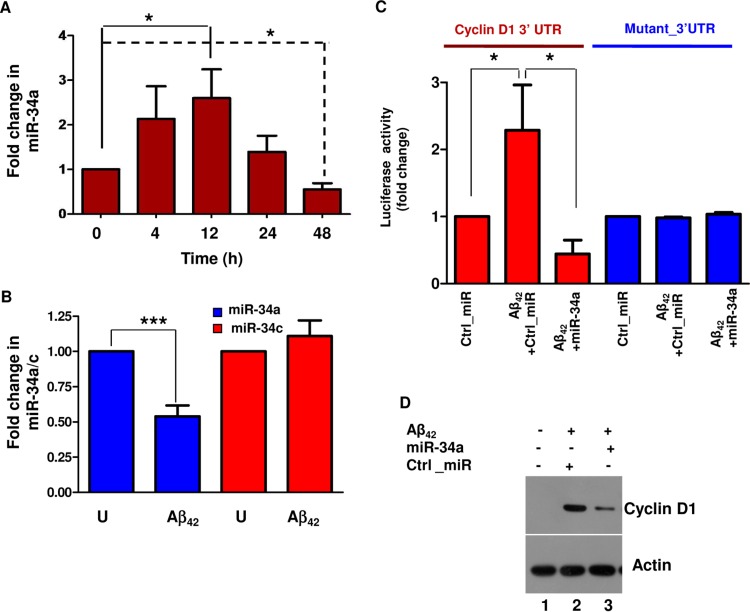
FIG 3.
Aβ42 downregulates miR-34a in cortical neurons, resulting in enhanced cyclin D1 production. (A) Rat cortical neurons were treated with Aβ42 for the indicated time. Total RNA was isolated and qRT-PCR was performed to determine the levels of miR-34a; data are presented as fold change in miR-34a expression with respect to untreated neurons (0 h). Data representative of three independent experiments are shown (*, P < 0.05, ANOVA; n = 3). (B) Rat cortical neurons were treated with Aβ42 for 48 h, and qRT-PCR was performed to determine the expression of miR-34a and miR-34c. Data are means ± SEM (***, P < 0.001, t test; n = 6). However, miR-34c remained almost unchanged after Aβ42 treatment. (C) Rat cortical neurons were transfected with the cyclin D1 3′ UTR or its mutant reporter plasmid along with miR-34a or Ctrl_miR and treated with Aβ42 for 48 h. Cell lysates were prepared, luciferase activity assays were performed, and fold change in activity with respect to Ctrl_miR-transfected cells was determined (*, P < 0.05, ANOVA; n = 3). (D) Rat cortical neurons were transfected with miR-34a or Ctrl_miR and treated with Aβ42 as indicated. Cell lysates were prepared after 48 h, and Western blotting for cyclin D1 was performed; β-actin was used as a loading control.