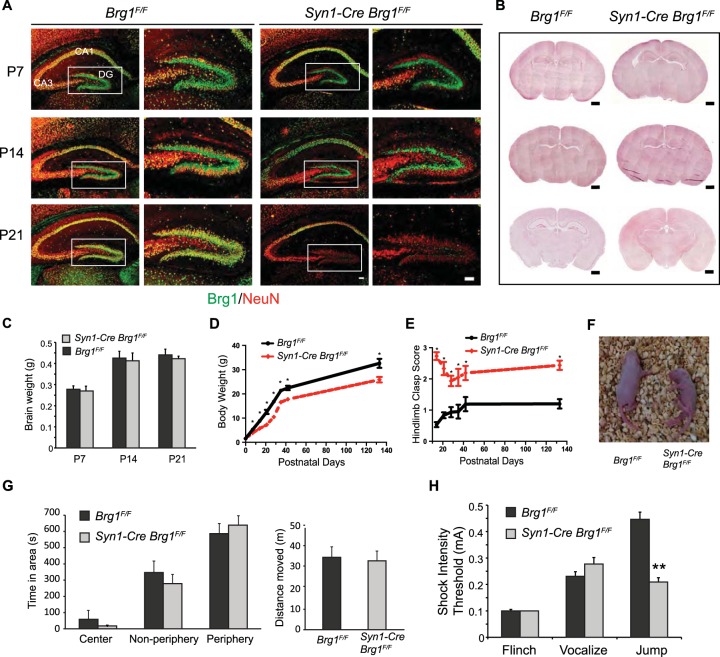
FIG 2.
Syn1-Cre-mediated Brg1 deletion in neurons led to neurological defects in mouse. (A) Syn1-Cre-mediated Brg1 deletion occurs in hippocampal neurons as indicated by costaining of Brg1 and the neuronal marker NeuN. Brg1 was present in all cells in Brg1F/F sections, whereas images from representative Syn1-Cre Brg1F/F mice show that Brg1 is not observed in NeuN+ DG granule neurons at P7 or in DG and CA3 regions at P14 and P21. Brg1 was intact in CA1 neurons. Scale bar, 100 μm. (B) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of coronal sections of Brg1F/F and Syn1-Cre Brg1F/F brains at different ages. Scale bar, 500 μm. (C) Brain weights of Brg1F/F and Syn1-Cre Brg1F/F mice during development (n = 3 in each group). (D) Body weights of Brg1F/F and Syn1-Cre Brg1F/F mice during development (n = 6, with matching numbers of male and females). (E) Hindlimb clasp scores of Brg1F/F and Syn1-Cre Brg1F/F mice during development (n = 6). Scoring is as follows: 0, both hindlimbs consistently splayed outward; 1, one hindlimb partially retracted; 2, both hindlimbs partially retracted; 3, both hindlimbs entirely retracted. Values in the graphs in panels D and E are shown as averages + standard errors. *, P < 0.01 (Student's t test). (F) Representative photograph of Brg1F/F and Syn1-Cre Brg1F/F pups at P7. The Brg1 mutant mouse displays a posture typical of the mutant pups indicative of difficulties righting to the face-down position. (G) Open-field activity tests were performed on adult Brg1F/F (n = 13) and Syn1-Cre Brg1F/F (n = 11) mice. No significant differences were found in either the distances moved or the preferences for the open-field areas in the full 15 min tested. (H) Foot shock test to determine the response threshold of Brg1F/F (n = 13) and Syn1-Cre Brg1F/F (n = 11) adult mice. Values in the graphs in panels G and H are shown as averages plus standard errors. **, P < 0.01 (Student's t test).