FIG 3.
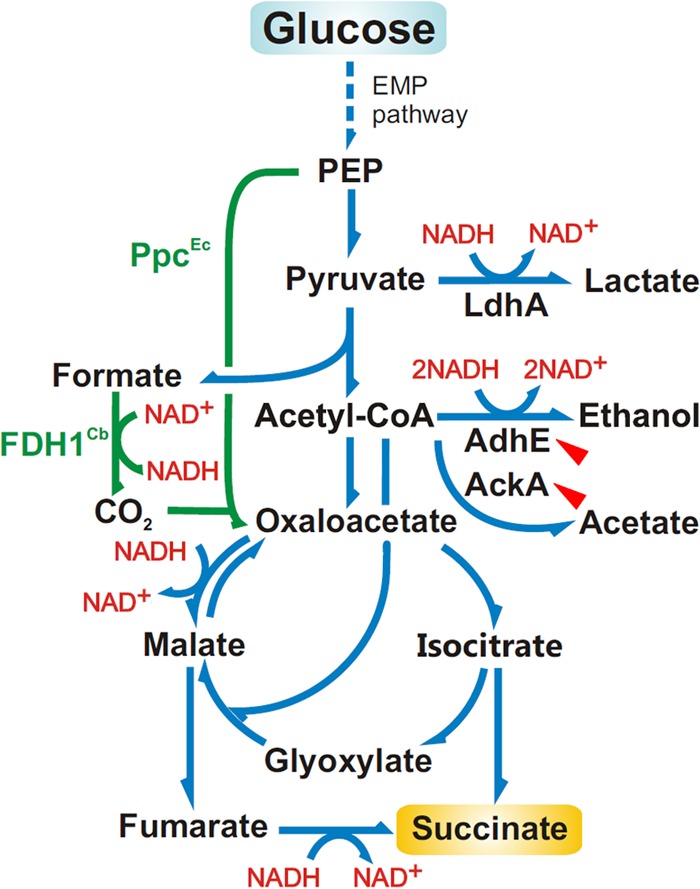
Diagram of the main metabolic pathways leading to succinate formation from glucose in E. coli. The genes encoding PpcEc (phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase) from E. coli and FDH1Cb (NADH-forming formate dehydrogenase) from C. boidinii were overexpresed in plasmids pEcPpc and pSBF2, respectively (the corresponding reactions are highlighted in green). The genes encoding AdhE (alcohol dehydrogenase) and AckA (acetate kinase) were knocked out in an attempt to enhance succinate accumulation (indicated by the red arrowheads). Note that several reactions within the biochemical network were grouped for the sake of simplicity. EMP pathway, Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas pathway; PEP, phosphoenolpyruvate; Acetyl-CoA, acetyl coenzyme A.
