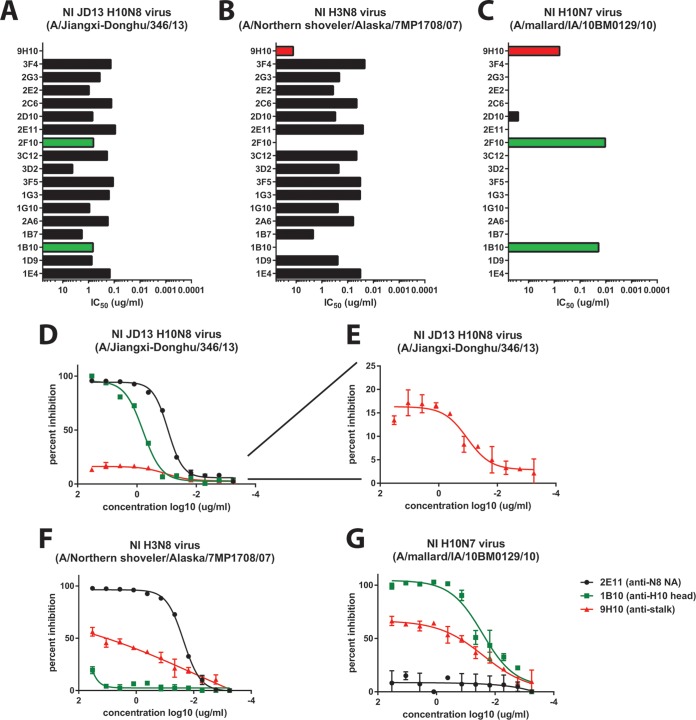
FIG 3.
Anti-HA head, anti-HA stalk, and anti-NA MAbs show NI activity. (A to C) All 18 MAbs generated (and 9H10) were tested in a classic neuraminidase inhibition (NI) assay, in which fetuin-coated ELISA plates were used as the target substrate. (A) N8 antibodies were able to significantly inhibit the NA activity of JD13 (H10N8) virus. (B) All anti-N8 antibodies were also able to significantly inhibit the NA activity of an H3N8 virus. Surprisingly, the anti-H10 antibodies displayed NI activity against JD13 (A) and an H10N7 strain (A/mallard/Interior Alaska/10BM01929/10) (C), and the anti-HA stalk antibodies displayed low—but significant—NI activity to both the H3N8 (A/Northern shoveler/Alaska/7MP1708/07) (B) and H10N7 (C) strains tested. To investigate this phenomenon, the NI data from one representative H10-reactive (1B10), N8-reactive (2E11), and the HA stalk-reactive antibody (9H10) were plotted and fit to nonlinear regression curves (D to G). At this resolution, it is apparent that 9H10 displays NI activity to H10N8 as well; this inhibition displays sigmoidal kinetics, but plateaus at only 15% maximal inhibition and so is not captured by the IC50 graph in panel A.