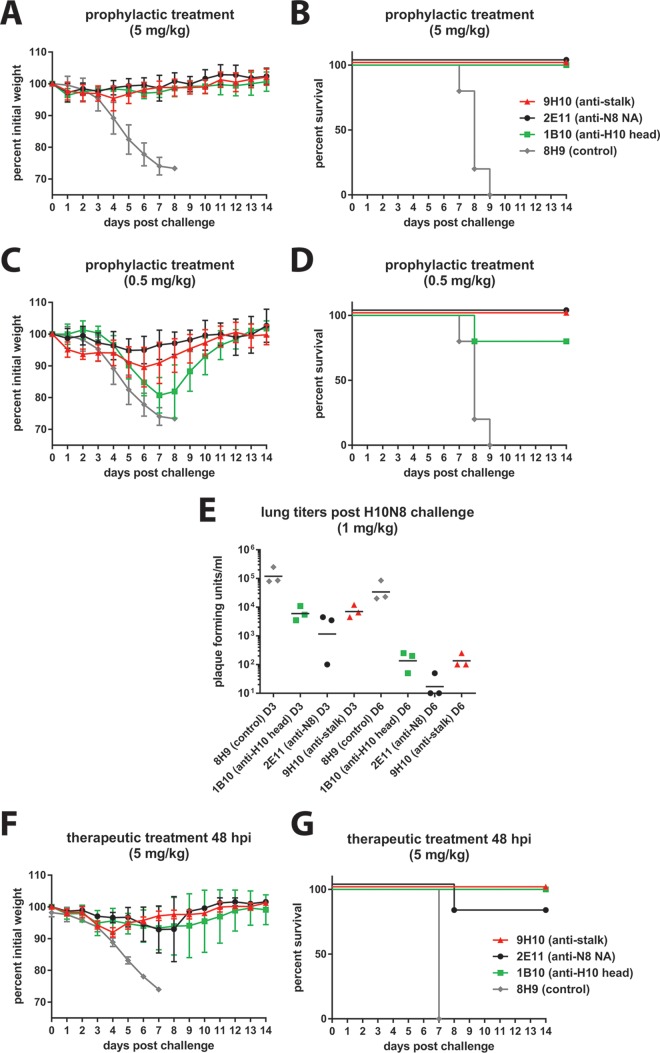
FIG 6.
Anti-HA head, anti-HA stalk, and anti-NA antibodies are protective against H10N8 in vivo. To test prophylactic efficacy, female BALB/c mice (5 per group) were administered either 5 or 0.5 mg/kg of a representative anti-H10 head (1B10), anti-H10 stalk (9H10), anti-N8 (2E11), or an irrelevant negative-control antibody (8H9, an anti-H6 head antibody) 2 h prior to a 5× LD50 challenge with JD13 (H10N8) virus. All antibodies (excluding the negative control) were protective against morbidity (A) and mortality (B) at the higher dose. At the lower dose, mice in the anti-N8 MAb group displayed the least weight loss (C), and all groups (except that receiving the anti-H10 head antibody) demonstrated 100% survival (D). The experimental results shown in panels A to D were performed in parallel and share the negative-control group. Prophylactic studies were repeated at a dose of 1 mg/kg, and mice were sacrificed at days 3 and 6 for lung titer analysis. (E) In line with previous weight loss results, the anti-N8 MAb was most effective in reducing titers at both time points. To test therapeutic efficacy, mice were administered 5 mg/kg of each antibody 48 h after a 5× LD50 challenge with JD13 (H10N8) virus. 1B10 and 9H10 were 100% protective, while 2E11 was 80% protective (F to G).