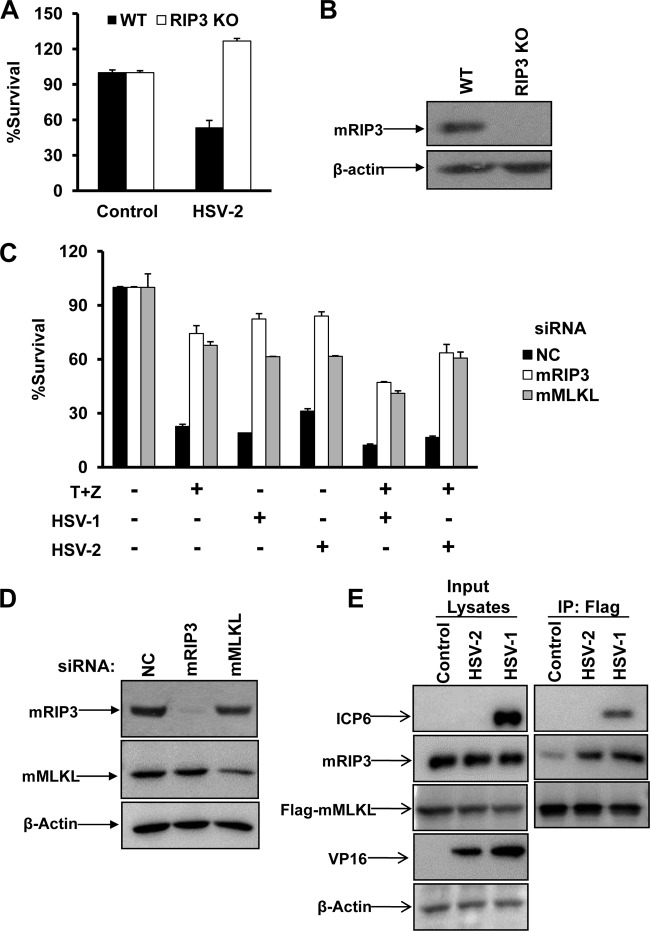
FIG 1.
HSV-2 as well as HSV-1 infection directly activates RIP3/MLKL-dependent necrosis in mouse cells. (A) Wild type (WT) and RIP3 knockout (KO) MEFs were infected with a control or HSV-2 at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 10 for about 20 h. Identical MOIs were used in MEFs in later experiments. Cell viability analysis was performed as described in Materials and Methods. (B) WT or RIP3 knockout MEF lysates were prepared and subjected to Western blot analysis. (C) L929 cells were transfected with a negative control (NC), mRIP3, or mMLKL siRNA oligonucleotide for 48 h. Then cells were treated as indicated for 15 h, and cell viability was determined. The HSV-1 MOI was 5. T, TNF-α (10 ng/ml); Z, Z-VAD (10 μM). (D) L929 cells were transfected with the indicated siRNA oligonucleotides for 48 h. Then cell lysates were prepared and subjected to Western blot analysis. (E) MEFs stably expressing Flag- and HA-tagged mMLKL were infected with HSV-1 or HSV-2 for 6 h. Cell lysates were prepared for immunoprecipitation with anti-Flag agarose beads. The Flag-mMLKL immunocomplex was then determined by Western blotting of the indicated proteins. IP, immunoprecipitation.