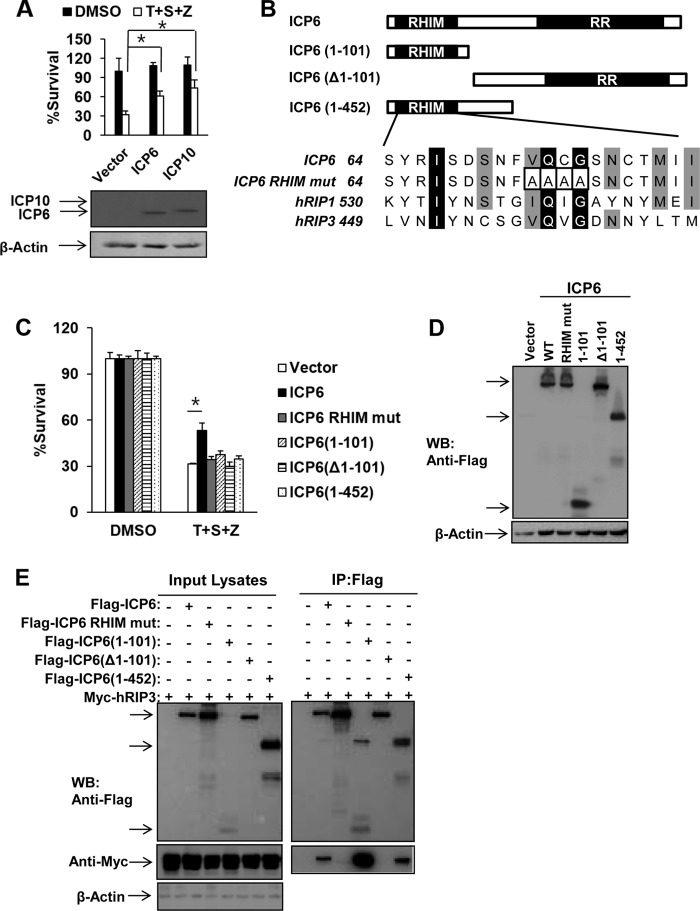
FIG 4.
Ectopic expression of HSV R1 is sufficient to block TNF-induced necrosis of human cells depending on both RHIM and RR domains. (A) HeLa-hRIP3 cells were transfected with empty vector or an ICP6 or ICP10 DNA plasmid for 24 h. Cells were treated with TNF-α/Smac mimetic/Z-VAD for an additional 36 h, and then cell viability was measured. Data represent the averages ± standard errors for three independent experiments. *, P < 0.05, versus results for the vector. Cell lysates were collected at 24 h posttransfection and subjected to Western blot analysis. (B) Domain structure of ICP6. Full-length ICP6 (amino acids 1 to 1137) contains the N-terminal RHIM domain and the C-terminal RR domain. ICP6(1–101) and ICP6(1–452) contain the N-terminal 101 residues and 452 residues, respectively. ICP6(Δ1–101) lacks residues 1 to 101. The residues 73 to 76 of ICP6 were mutated to four alanine residues. (C and D) HeLa-hRIP3 cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids for 24 h. Cells were treated with TNF-α/Smac mimetic/Z-VAD for an additional 36 h, and then cell viability was measured (C). Data represent the averages ± standard errors for three independent experiments. *, P < 0.05, versus results for the vector. Cell lysates were collected at 24 h posttransfection and subjected to Western blot analysis (D). (E) 293T cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids for 48 h. Cell lysates were collected and immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag agarose beads. The immunoprecipitate was analyzed by Western blotting (WB).