Fig. 4.
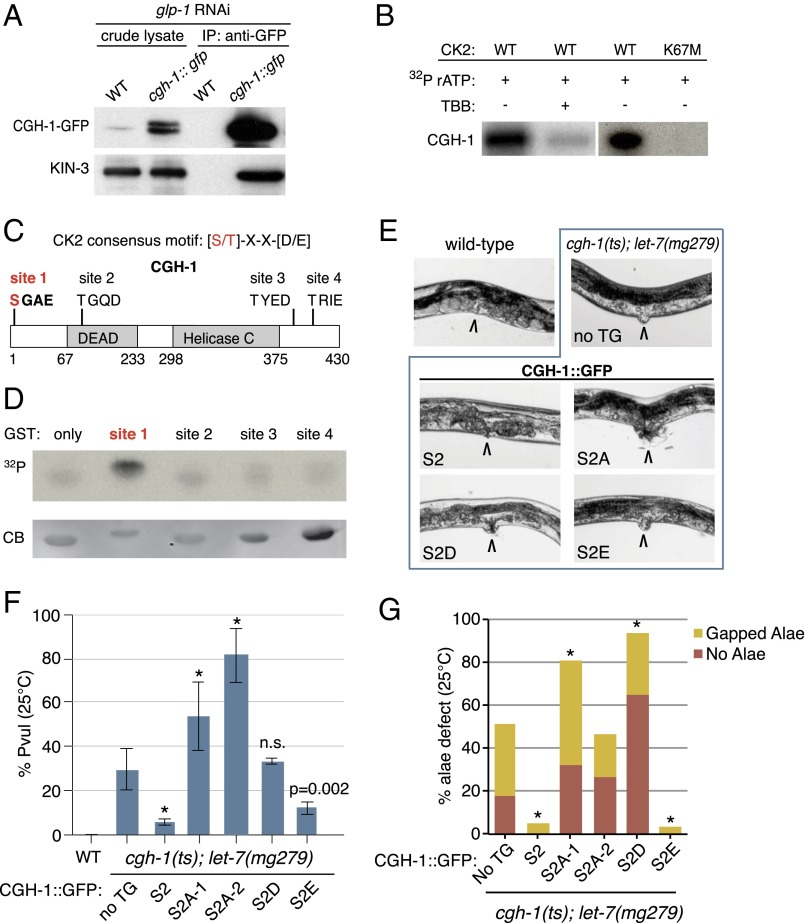
CK2 phosphorylates miRISC factor CGH-1 at serine 2. (A) KIN-3 associates with CGH-1 in the soma. CK2 catalytic subunit, KIN-3, coimmunopurifies with CGH-1::GFP in L4 stage animals fed glp-1 RNAi to prevent germ-line proliferation. (B) CGH-1 is phosphorylated by CK2 in vitro. Autoradiogram of GST-purified wild-type CGH-1 incubated with GST-purified CK2 composed of wild-type or ATP-binding site mutant KIN-3 (K67M). TBB, CK2 inhibitor (4,5,6,7-tetrabromobenzotriazole). (C) CGH-1 harbors four CK2 recognition motifs (sites 1–4). (D) Site 1 (serine 2) is phosphorylated by CK2 in vitro. GST-tagged CGH-1 peptides composed of 20 residues flanking each putative CK2 phosphorylation site were incubated in vitro with CK2 and analyzed by SDS/PAGE and autoradiography. 32P, autoradiogram; CB, Coomassie Blue stained gel. (E and F) Genetic analysis of CGH-1 serine 2 (S2) phosphovariants in cgh-1(tn691)ts; let-7(mg279) suggests phosphorylation of CGH-1 at S2 promotes miRISC function (E) Representative images of Protruding vulva (Pvul). Adult vulva indicated by arrow (120 h post-L1, 25 °C). (F) Quantitation of Pvul. Compared with cgh-1(tn691)ts; let-7(mg279) with no transgene the cgh-1::gfp (S2) transgene significantly rescues Pvul. S2A mutants (lines 1 and 2) significantly enhance Pvul (two-tailed Fisher’s exact test *P < 0.0001 for S2 variants versus “no TG,” mean and SD plotted for three technical replicates within a single experiment, n ≥ 95). (G) S2 and S2E significantly rescue alae defects of cgh-1(tn691)ts; let-7(mg279). S2A mutants significantly enhance (line 1) or have no significant effect (line 2) on defects (two-tailed Fisher’s exact test *P < 0.0001 for S2 variants versus “no TG”). TG, transgene; S2A lines 1 and 2, phosphodefective Ser-to-Ala mutation; S2D/E, phosphomimic Ser-to-Asp/Glu mutations.