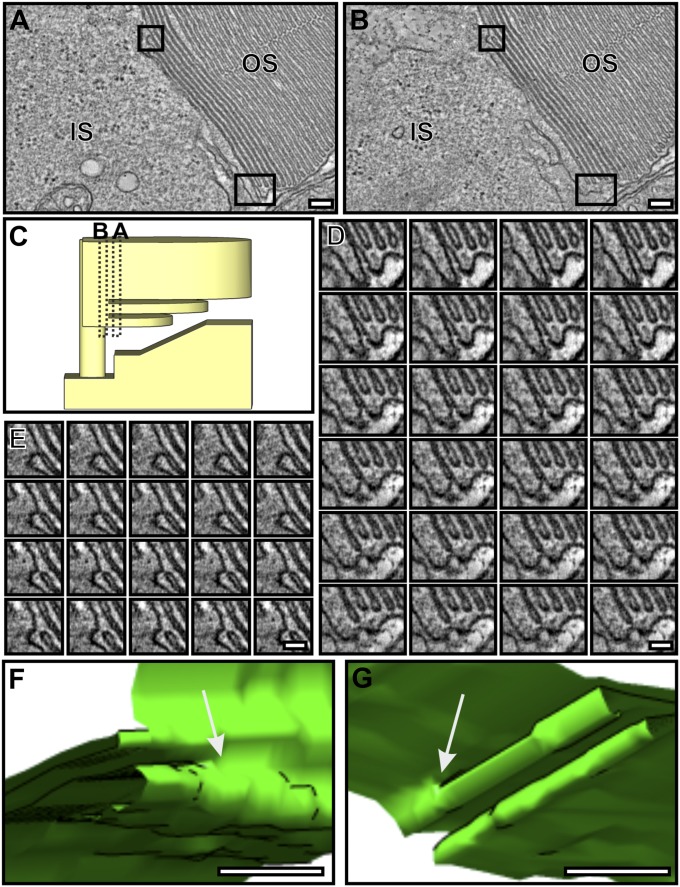
Fig. 4.
Discrete discs are formed by the fusion of adjacent OS plasma membrane evaginations. (A and B) Two different slices from the same tomogram of a mouse rod photoreceptor. (C) The predicted position of the tomogram slices in A and B. The boxed regions in A show membrane that is open to the extracellular environment and fused in B. (D and E Montage of the tomogram slices corresponding to the boxed regions in A and B; the transition from open to closed membrane and the point of fusion between the adjacent plasma membrane to form a new disk is apparent. (F and G) Models generated from D and E showing the point of plasma membrane fusion in 3D. (Scale bars, A and B, 100 nm; D and E, 50 nm; F and G, 20 nm.)