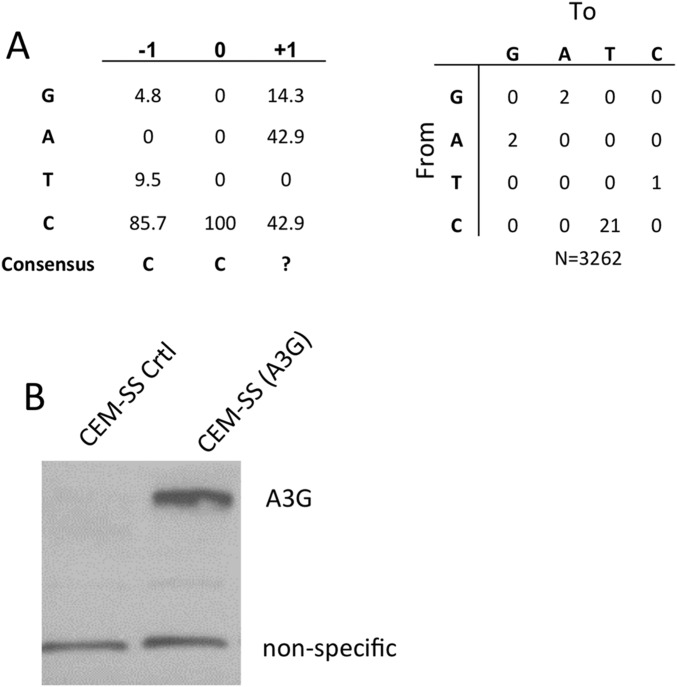
Fig. S4.
Infection of a polyclonal CEM-SS cell line expressing endogenous A3G. (A) A total of 2 × 106 293T cells were transfected with 10 µg of HIV-1-NLuc-WT or HIV-1-NLuc-ΔVif. Virus containing supernatants were passed through a 0.45-µm filter and the virus was then used to infect the polyclonal cell lines CEM-SS(A3G) or CEM-SS(CTRL) at a concentration of 105 cells/mL in a total volume of 5 mL. Cells were visually monitored for cell proliferation. After 2 wk the CEM-SS(CTRL) cells infected with either HIV-1-NLuc-WT or HIV-1-NLuc-ΔVif were determined to be nonviable. The CEM-SS(A3G) cells infected with HIV-1-NLuc-WT also contained few, if any, viable cells. However, the CEM-SS(A3G) cells infected with HIV-1-NLuc-ΔVif were actively growing. After an additional week in culture, total DNA was isolated from CEM-SS(A3G) cells infected with HIV-1-NLuc-ΔVif using a DNeasy kit (Qiagen). A region of HIV-1 proviral DNA was PCR amplified and cloned, sequenced, and analyzed for A3G-induced C-to-T mutations in the (−) strand HIV DNA. (B) Expression of endogenous A3G in polyclonal CEM-SS(A3G) cells was confirmed by Western blot, as described above.