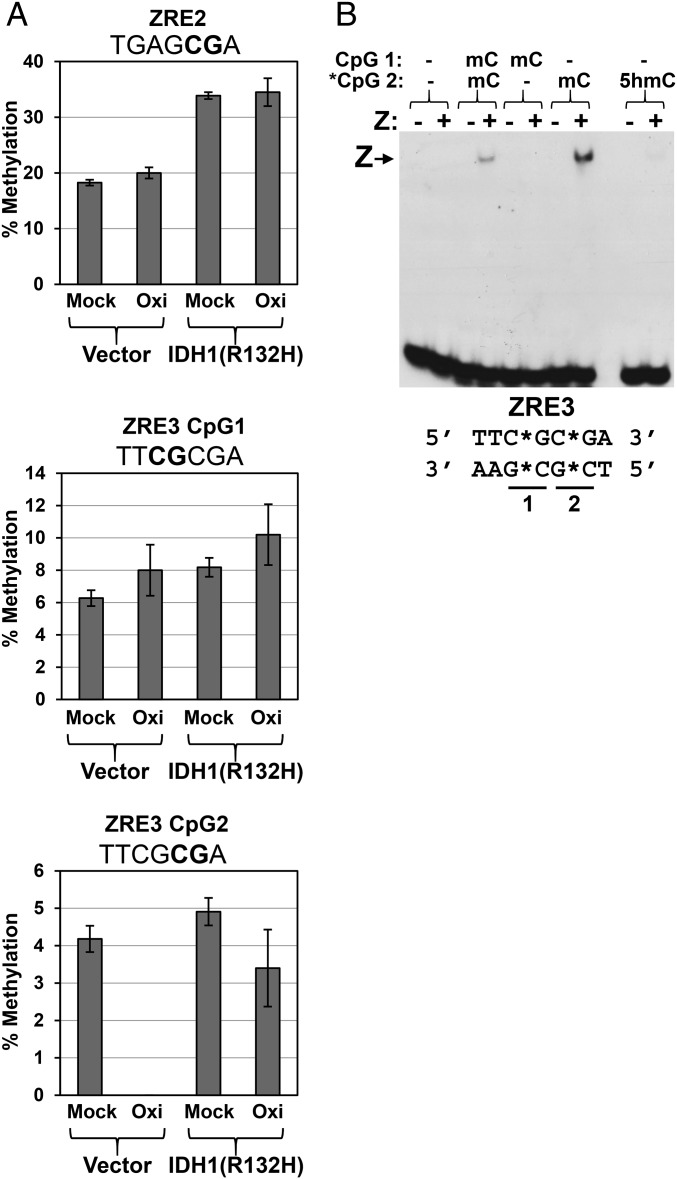
Fig. 7.
The R promoter ZRE3 site is 5-hydroxymethylated in EBV-infected NOKs via a TET-dependent mechanism. (A) DNA was isolated from EBV-positive NOKs infected with either the retrovirus control vector or the IDH1(R132H)-expressing retrovirus, and then the DNA was either mock-treated (Mock) or oxidized with KRuO4 (Oxi), followed by bisulfite conversion and pyrosequencing as described in Materials and Methods. The sequences of each ZRE motif are shown above the respective graph, with the CpG sites bolded; the two adjacent CpGs in ZRE3 are numbered 1 and 2. The error bars indicate SE calculated from two replicate experiments where each sample was pyrosequenced in triplicate. (B) The ability of Z to bind to the Rp ZRE3 site containing various patterns of methylation and 5-hydroxymethylation was examined using EMSA; the cytosine modification status in each lane is shown above the EMSA image. Z–DNA complexes are indicated with an arrow.