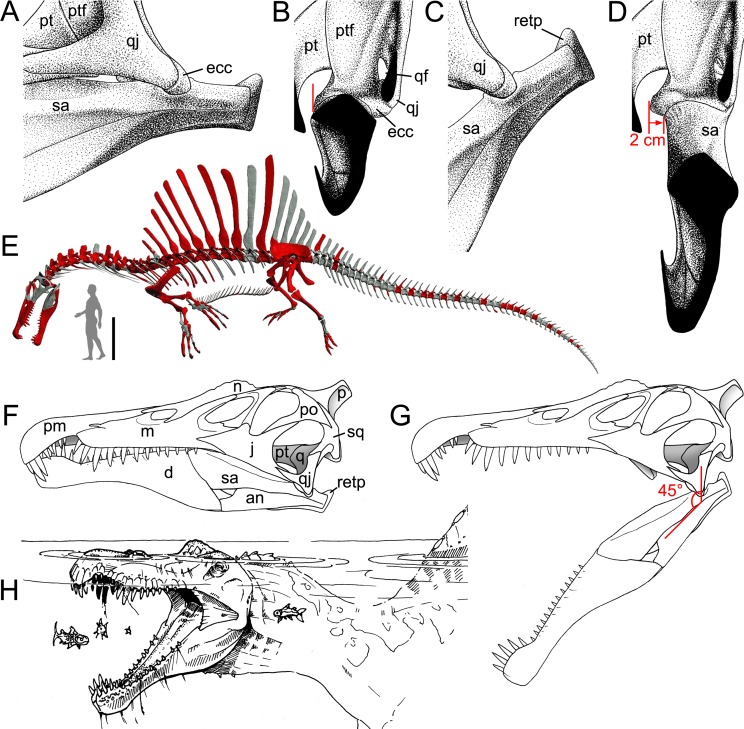
Fig 15. Jaw mechanics in the spinosaurid Spinosaurus.
A–D, Mandibular articulation; and F, G, skull in A, C, F–G, lateral; and B, D, anterior views; when A–B, F, the mouth is closed; and C–D, G, fully open, illustrating the lateral movement (in red) of the mandibular ramus for a 45° rotation of the lower jaw (courtesy of Jaime A. Headden); E, skeletal reconstruction of Spinosaurus aegyptiacus by Ibrahim et al. [22]) in swimming position in lateral view with a human (1.8 m) as a scale (modified from Ibrahim et al. [22]). This model is based on spinosaurid cranial and postcranial remains (colored in red) from the Albian-Cenomanian of Northern Africa which possibly belong to two spinosaurine taxa (see also Evers et al. [27]); H, reconstruction of a semi-aquatic Spinosaurus in fishing position (i.e., jaws wide open) in anterolateral view (courtesy of Jason Poole). Abbreviations: an, angular; ar, articular; d, dentary; ecc, ectocondyle; enc, entocondyle; j, jugal; m, maxilla; n, nasal; p, parietal; pm, premaxilla; po, postorbital; pt, pterygoid; ptf, pterygoid flange; q, quadrate; qf, quadrate foramen; qj, quadratojugal; retp, retroarticular process of the articular; sa, surangular; sq, squamosal.