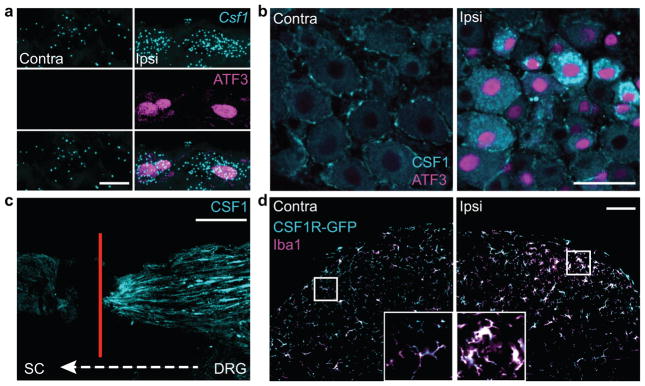
Figure 2. CSF1 is de novo induced in injured sensory neurons and transported to the spinal cord, where CSF1R is expressed exclusively in microglia.
(a) Co-expression of Csf1 mRNA (in situ hybridization) and ATF3 (immunostaining) in injured DRG neurons (1d post injury), compared to contralateral side. Scale bar: 10 μm; (b) Compared to the contralateral side, there is de novo CSF1 (immunostaining) in axotomized, ATF3 positive DRG neurons (1d post injury). Note that there is mild CSF1 immunoreactivity in satellite cells. Scale bar: 50 μm; (c) Concurrent L4 and L5 dorsal root ligation and peripheral nerve injury results in the accumulation of CSF1 protein (immunoreactivity) at the dorsal root ligature (4d post surgery). Red line denotes ligature site (see Fig. 1a). Scale bar: 200 μm; (d) Complete overlap of the microglial markers, Iba1 and GFP in the dorsal horn of a CSF1R-GFP reporter mouse. Both markers increase in the dorsal horn ipsilateral to the nerve injury (3d post injury) compared to the contralateral side. Inset: Control (left) and activated (right) microglia. Note the amoeboid morphology of activated microglia. Scale bar: 100 μm. Inset: maximum projection of Z-stack images.