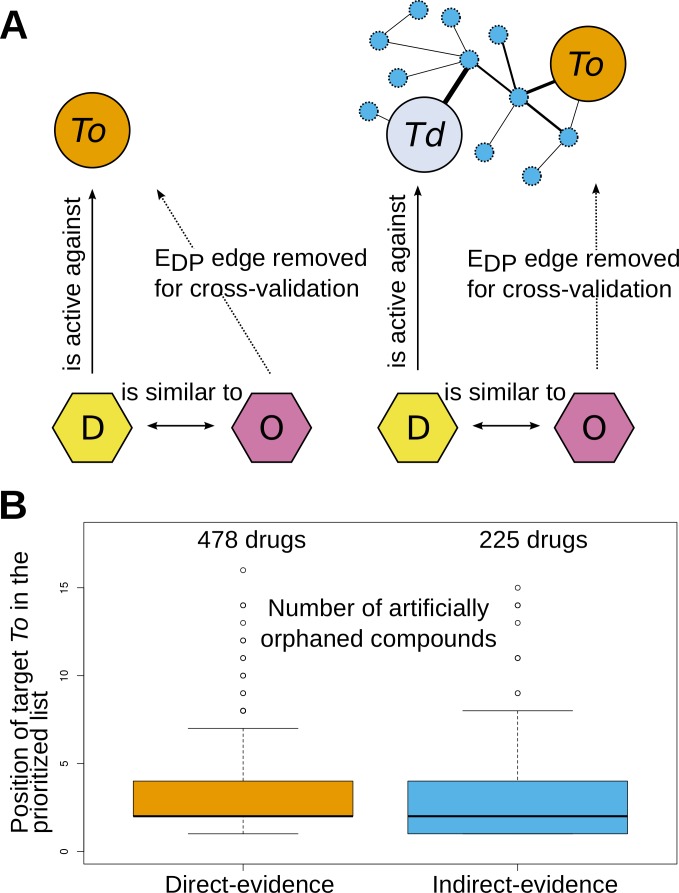
Fig 4. Inference of targets of orphaned compounds.
a, top: Schematic view of two different ways in which the algorithm can find the correct target for artificially orphaned compounds. O = orphan compound; D = bioactive drug/compound which is a first neighbor of O in the D-layer; To, known target of the artificially orphaned compound O; Td, known target of compound D. Arrows represent significant similarity relationships between compounds or significant bioactivity links between a target and a compound. Dashed lines connecting compounds and targets represent the original EDP edges that were removed for the cross-validation procedure. a, left: direct inference, compound D has a bioactivity link to To (special case, To = Td). a, right: indirect inference, compound D lacks bioactivity links against To, but a high-scoring path connects Td to To in the projected PP-layer. b, bottom: boxplots showing the distribution of the position of To targets in the rankings for 703 orphaned compounds. b, left: boxplot for cases that fell in the direct inference class (478 compounds). b, right: boxplot for cases in the indirect inference class (225 compounds).