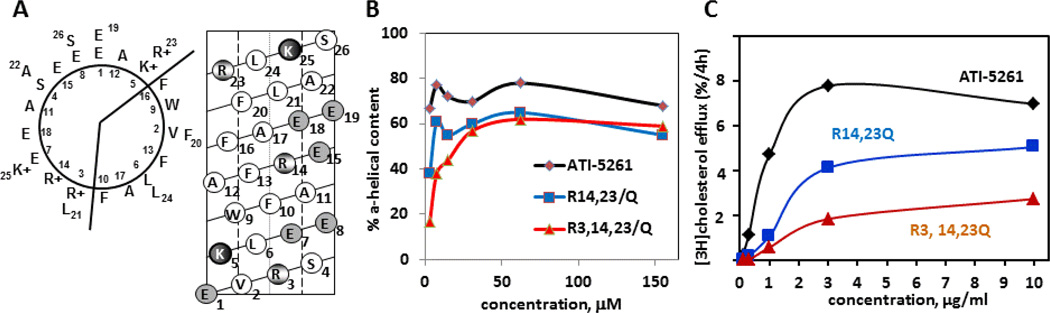
Figure 1. Secondary structure and activity of ABCA1 agonist peptide ATI-5261.
Panel A (left diagram) shows the primary amino acid sequence of ATI-5261 on a helical wheel diagram. Position 1 corresponds to the first amino acid. The peptide forms a class A amphipathic α-helix, with cationic amino acids located at the lipid water-interface and negatively charged residues positioned in the middle of the polar surface. The helical net diagram in Panel A (right) depicts the ATI-5261 α-helix cut down the center at position 1, then flattened. Salt-bridges are located between negatively charged amino acids (shaded circles) and cationic residues (partially shaded) at positions E1-K5, R3-E7, R14-E18, and E19-R23. Panel B - ATI-5263 is able to retain a high α-helical content as the peptide is diluted from 500 - 10 µg/ml (310 - 6 µM), under conditions that favor dissociation of oligomer forms to individual peptide strands (14, 16). In contrast, the R→Q variants of ATI-5261 failed to retain α-helix structure upon dilution, indicating salt bridge interactions were required to stabilize the secondary structure. The high α-helical content observed with increasing peptide concentration is typically attributed to peptide self-association. Panel C- Peptides with R→Q substitutions are poor mediators of cholesterol efflux, as determined using J774 macrophages treated with cAMP to up-regulate ABCA1. Data were redrawn from ref 16.