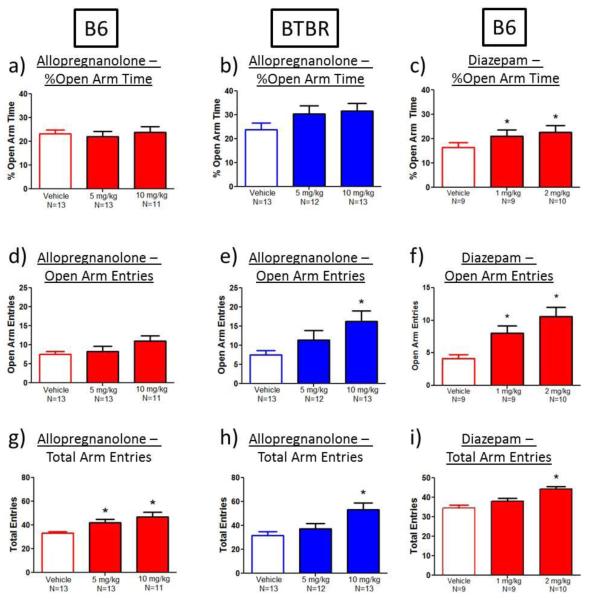
Fig. 7.
A standard benzodiazepine anxiolytic, diazepam, produced a selective anxiolytic-like effect on the elevated plus-maze, while the neurosteroid, allopregnanolone, did not. a-b) Allopregnanolone administration did not significantly increase percent open arm time in B6 or BTBR mice. c) Diazepam administration (1 and 2 mg/kg) significantly increased percent open arm time in B6 mice. d-e) Allopregnanolone administration did not significantly increase open arm entries in B6 mice, but did increase open arm entries in BTBR mice (10 mg/kg). f) Diazepam administration (1 and 2 mg/kg) significantly increased open arm entries in B6 mice. g-h) Allopregnanolone administration (5-10 mg/kg) increased total entries in B6 and BTBR mice. i) A standard dose of diazepam (1 mg/kg) which showed anxiolytic-like effects on open arm time and open arm entries, did not affect total number of arm entries, although a high dose of diazepam (2 mg/kg) increased total arm entries in B6 mice. *p<0.05, as compared to vehicle