Fig. 2.
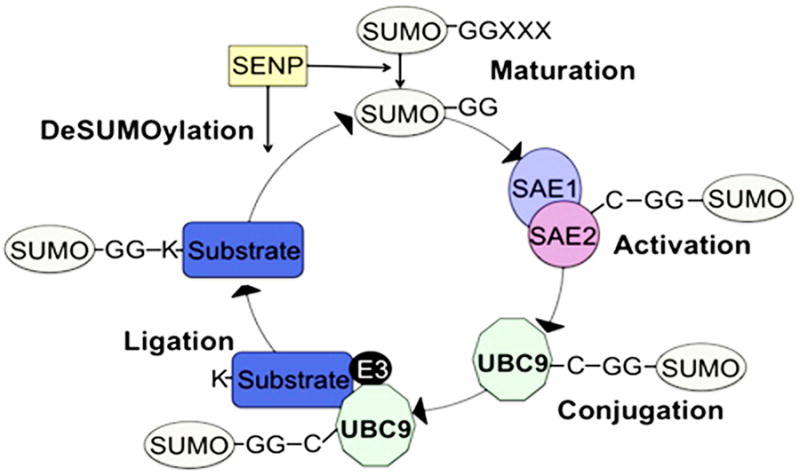
The SUMOylation reaction. The covalent attachment of SUMO proteins to specific lysine residues within substrate proteins is carried out in three enzymatic steps: 1) After SENP-mediated proteoloytic processing of the inactive SUMO precursor, SUMO is activated to the mature SUMO form by the E1 activating heterodimer, 2) SUMO is then conjugated to the E2 conjugating UBC9, and 3) E3 ligases can interact with UBC9 to facilitate SUMO ligation to substrate proteins. SUMO can be reversibly removed by the SENP proteins.
