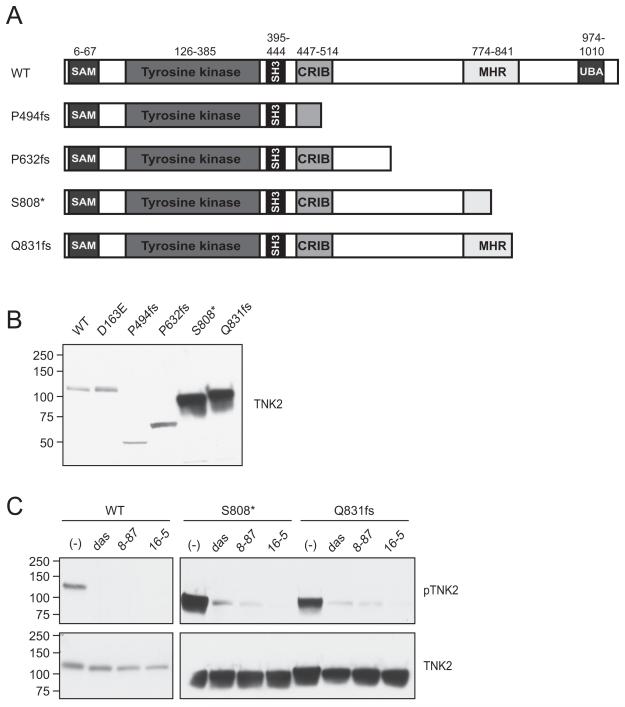
Figure 7. TNK2 truncation mutations found in solid tumors are sensitive to TNK2 inhibitors.
(A) Schematic of a subset of TNK2 truncation mutations found in solid tumors. (B) TNK2 S808* and Q831fs mutations result in protein overexpression. TNK2 mutations were transiently transfected into 293T17 cells and then total TNK2 levels were measured using an antibody to the TNK2 N-terminus. The TNK2 S808* and Q831fs were noticeably overexpressed compared to WT TNK2 or the other TNK2 truncations. (C) Phosphorylation of TNK2 mutants is inhibited by dasatinib, XMD8-87 and XMD16-5. 293T17 cells were transiently transfected with WT TNK2, TNK2 S808* or TNK2 Q831fs. After 48 hours the cells were treated with 1 μM dasatinib (das), 2.5 μM XMD8-87 or 2.5 μM XMD16-5 for 3.5 hours, and then harvested and subjected to immunoblot analysis for phosphorylated TNK2 (pTNK2) or total N-terminal TNK2. Drug concentrations were chosen based on the inhibition of WT TNK2 phosphorylation shown in figure 4D. Blots for WT and mutant TNK2 were run simultaneously, under the same conditions and exposed for identical time. These experiments were repeated with similar results.