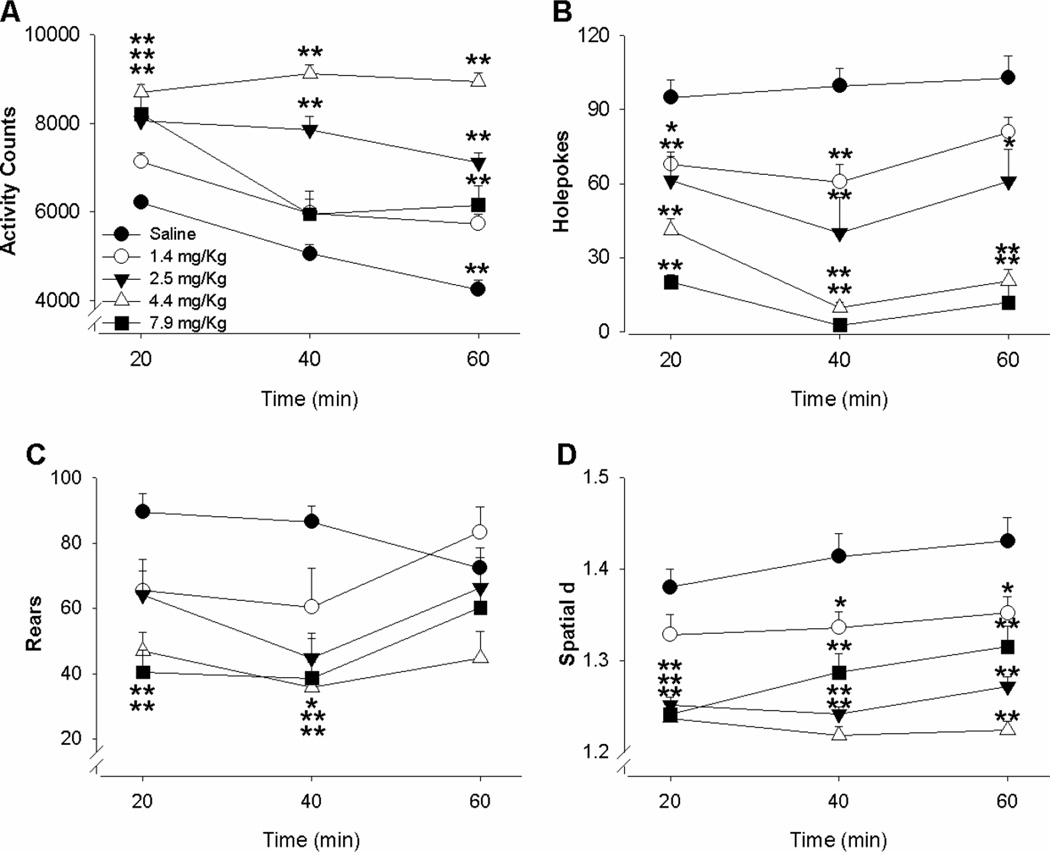
Figure 2. Effects of d-amphetamine in mice in the BPM.
The effects of d-amphetamine on exploratory behavior in mice measured using the mouse behavioral pattern monitor (BPM). Male and female C57BL/6J mice (n=40 per sex) were treated with vehicle or d-amphetamine (1.4, 2.5, 4.5, or 7.9 mg/kg; n=8 per dose) immediately prior to their introduction to the mouse BPM. Amphetamine treatment significantly increased activity (a), while reducing holepoking (b), rearing (c), and lowering spatial d (d), in mice irrespective of sex. These effects were seen in each domain even at the lowest dose, except on activity levels. Data presented as mean + SEM, *p < 0.05 compared to saline, **p < 0.01 compared to saline