Figure 1. Model of TLR signaling with select negative regulators.
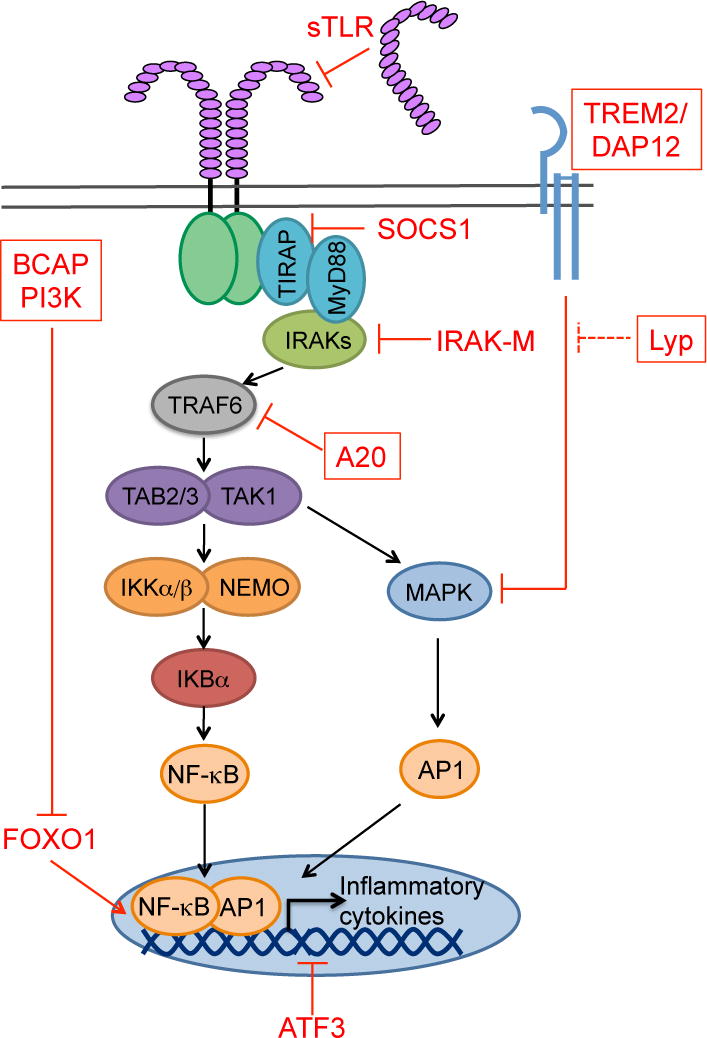
MyD88-dependent TLR signaling can be inhibited at any step along the signaling pathway. We have highlighted in red text select inhibitors that exemplify inhibition at different steps of the pathway. Those in a red box are discussed further in this review. For example, soluble forms of TLR2 and TLR4 inhibit signaling by blocking ligand binding to the TLR. SOCS1, A20 and IRAK-M block key steps in signal transduction downstream of most TLR (A20 and IRAK-M) or TLR4 (SOCS1). ATF3 is a transcription factor that dampens the transcription of inflammatory genes by recruiting histone deacetylases to the promoters of pro-inflammatory genes. BCAP is a signaling adapter that inhibits TLR signaling through PI3-kinase (PI3K) activation. One downstream mediator of PI3K inhibition of TLR responses is the transcription factor FOXO1, whose removal from the nucleus helps terminate transcription of some pro-inflammatory genes. The TREM2/DAP12 receptor signals in response to endogenous glycoproteins and lipids, thereby sensing the extracellular milieu of the macrophage. Signaling through TREM2/DAP12 inhibits TLR responses through reducing MAPK (Erk1/2) activation. Here we propose this pathway is regulated by the tyrosine phosphatase Lyp.
