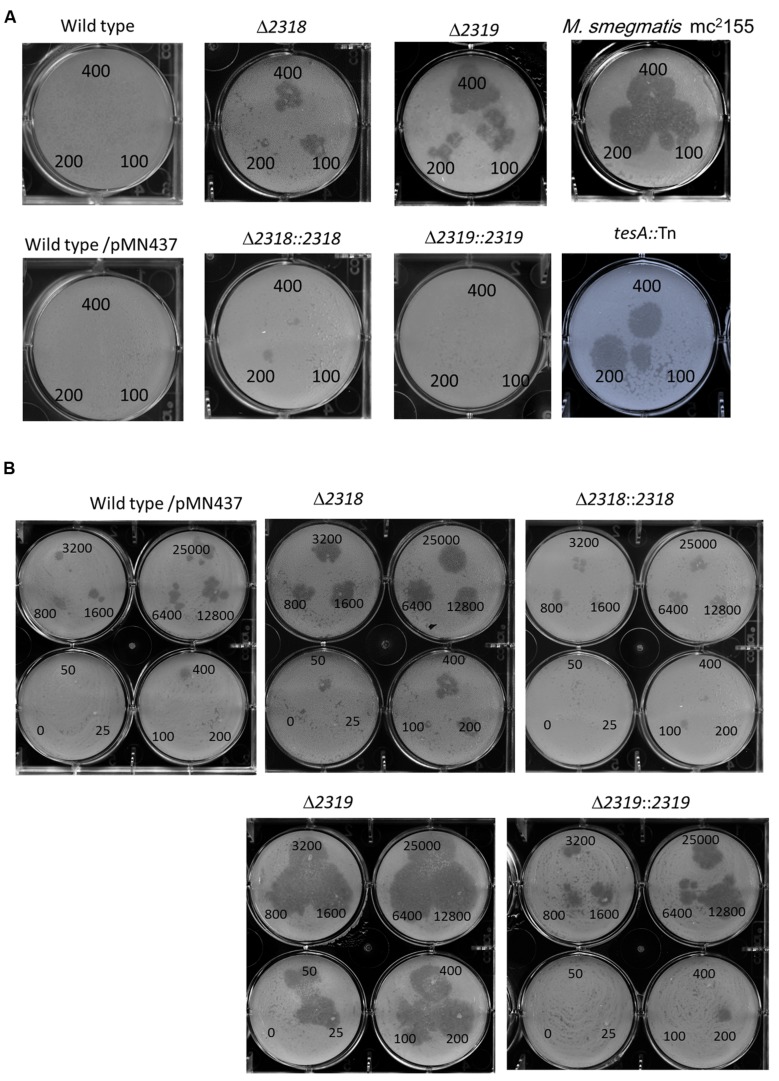
FIGURE 4.
Phenotypic confirmation and quantitative analysis of deletion mutants and complementation strains. (A) The Dictyostelium phagocytosis plaques on bacterial lawn with the wild-type, deletion, and complementation strains. A total of 400, 200, or 100 Dictyostelium cells could form a clear phagocytosis plaque on a bacterial lawn with Δ2318 and Δ2319 mutants but not with the wild-type, Δ2318::2318 and Δ2319::2319 strains. M. smegmatis mc2155 and tesA::Tn mutant (known as an avirulent M. marinum mutant) were served as controls. Comparable results were observed in wild type vs. wild type/pMN437, demonstrating that the transfer of pMN437 into M. marinum did not affect phagocytic plaque formation. (B) Quantitative analysis of virulence of wild-type, deletion, and complementation strains. Different amounts of Dictyostelium (0–25000 cells) were used to quantify the virulence of the M. marinum wild-type strain, the deletion mutants (Δ2318 and Δ2319), and the complementation strains (Δ2318::2318 and Δ2319::2319). Fifty cells and twenty-five Dictyostelium cells could form a clear phagocytic plaque on bacterial lawn with the Δ2318 and Δ2319 mutants, respectively, but not with the wild-type, Δ2318::2318 and Δ2319::2319 strains. The virulence phenotype was restored (>400 cells) in the complementation strain.