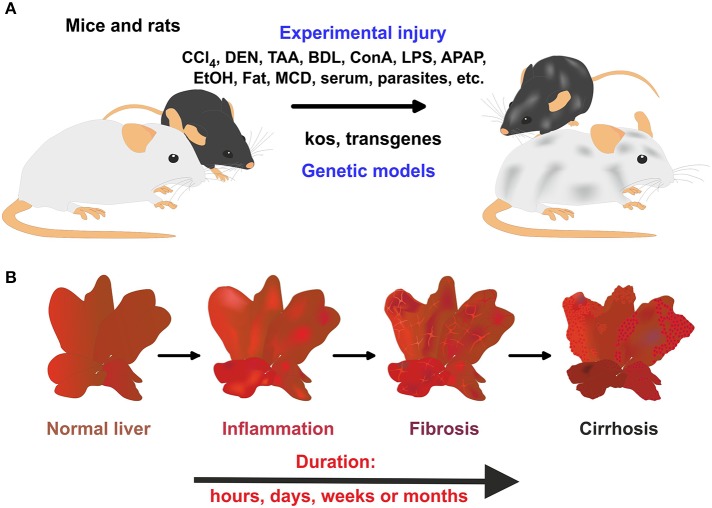
Figure 1.
Rodent models in experimental liver fibrosis. (A) The application of hepatotoxins or parasites, bile duct surgery, or the feeding of specialized diets is widely applied to induce liver damage and hepatic fibrogenesis in mice and rats. In addition, genetically engineered mice models that develop spontaneous hepatic fibrosis are further alternatives. (B) In these models, a time-dependent progress of liver damage occurs in which inflammation, fibrosis, and cirrhosis time-dependently follow each other.