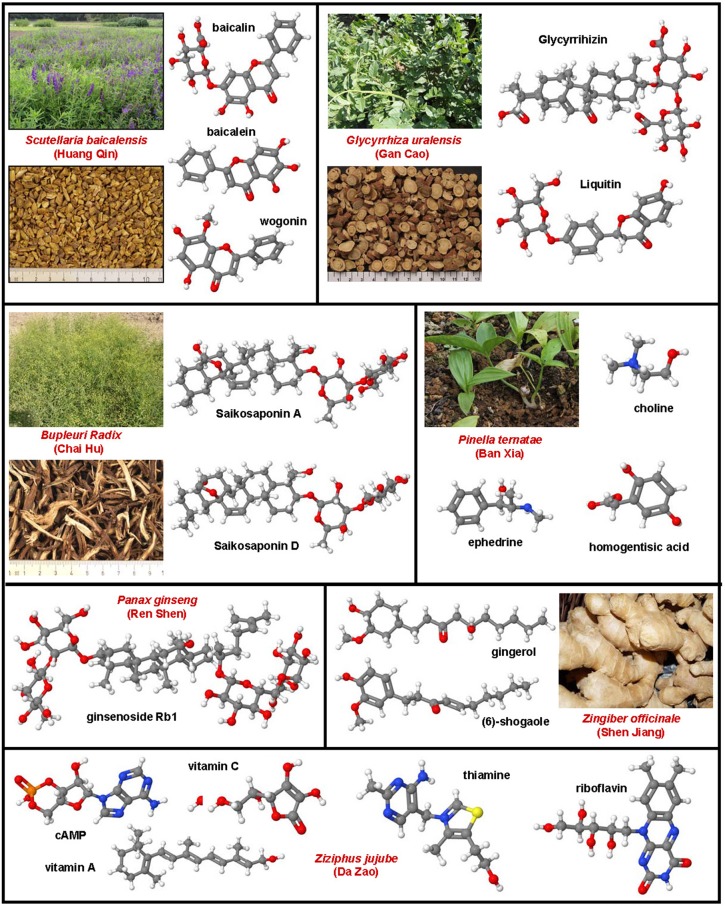
Figure 9.
Sho-shaiko-to a herbal mixture and its main ingredients. Sho-saiko-to contains root of Bupleurum, root/stolon of Glycyrrhiza, root w/o rootlets of Panax ginseng, tuber w/o cork layer of Pinelliae, rot w/o periderm of Scutellaria, root/rhizome of Zingiber, and fruit of Ziziphus jujube. Each herb contribute some key ingredients that together are made responsible for the antifibrotic activity of Sho-saiko-to. Bupleurum contains different Saikosaponins (e.g., Saikosaponin A, CAS 20736-09-8; Saikosaponin D, CAS 20874-52-6), while licorice is enriched with the glycyrrihizin (CAS 1405-86-3) and liquiritin (CAS 551-15-5). Ginseng contains different ginsenosides and panaxic acid. Pinellia is enriched with homogentisic acid (CAS 451-13-8), ephedrine (CAS 299-42-3), and choline (CAS 67-48-1). Baical skullcap contains baicalin (CAS 21967-41-9), baicalein (CAS 491-67-8), and wogonin (CAS 632-85-9). The active components of ginger are gingerol and shogoal. Jujube is enriched in cyclic AMP (CAS 60-92-4), vitamin C (CAS 50-81-7), vitamin A (CAS 68-26-8), niacin (CAS 59-67-6), riboflavin (CAS 83-88-5), and thiamine (CAS 59-43-8). The plant images were provided by Dr. Heidi Heuberger (LfL, Bayerische Landesanstalt für Landwirtschaft, Freising, Germany, www.lfl.bayern.de/).