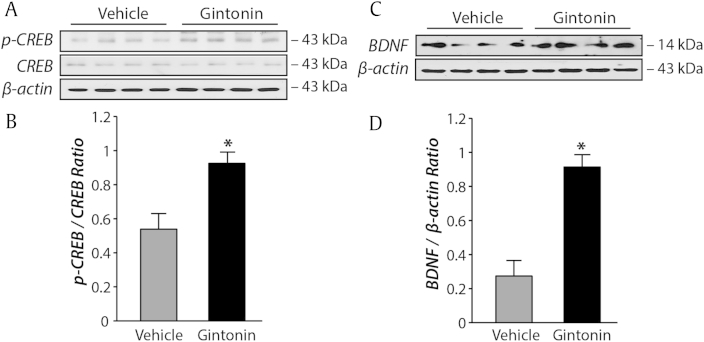
Fig. 4.
Gintonin administration increases hippocampal cyclic adenosine monophosphate-response element binding (CREB) phosphorylation and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) expression. (A) Representative immunoblots of hippocampal CREB and phosphorylated CREB (p-CREB). (B) CREB and p-CREB levels were quantified 30 min after testing in the contextual fear conditioning paradigm. Data are expressed as the ratio between p-CREB/CREB. There was a significant increase in p-CREB in gintonin-administered mice when compared with vehicle-administered mice (n = 7–8, *p < 0.05). (C) Representative immunoblots of hippocampal BDNF. (D) Data are expressed as the ratio between BDNF/β-Actin. Overall hippocampal BDNF expression was significantly higher in gintonin-administered mice when compared with vehicle-administered mice (n = 7–8, *p < 0.05). Error bars represent standard error of the mean.