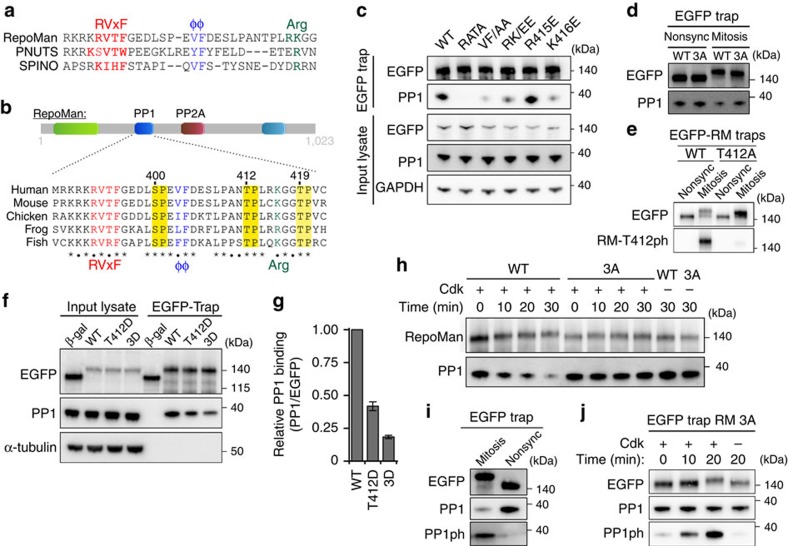
Figure 3. Cdk1 reduces the activity of PP1-RepoMan.
(a) Sequence alignment of the PP1-interaction domains of RepoMan, PNUTS and Spinophilin. (b) Conservation of the PP1-interaction domain of RepoMan in vertebrates. (c) EGFP traps from HEK293T cells expressing the indicated EGFP-RepoMan mutants were analysed by immunoblotting for the binding of PP1. (d) U2OS cells were transfected with EGFP-tagged RepoMan-WT or RepoMan-3A. EGFP traps from non-synchronized (Nonsync) or Nocodazole-arrested (Mitosis) U2OS cell lysates were examined for associated PP1. (e) U2OS cells were transfected with EGFP-tagged RepoMan-WT. EGFP traps from Nonsync or Nocodazole-arrested (Mitosis) U2OS cell lysates were examined for EGFP and RepoMan-T412ph antibody. (f) EGFP traps from non-synchronized HEK293T cells expressing EGFP-tagged β-galactosidase (β-gal), RepoMan-WT, RepoMan-T412D or RepoMan-3D were analysed by immunoblotting for associated PP1. (g) The PP1/EGFP ratio was quantified by densitometric analysis. The data represent means±s.e.m. from three independent experiments. (h) EGFP traps from non-synchronized HEK293T cells expressing EGFP-tagged RepoMan-WT or RepoMan-3A were phosphorylated in vitro with recombinant Cdk2/Cyclin A. Unbound PP1 was washed away before the addition of SDS sample buffer to the traps and immunoblotting for PP1. (i) Phosphorylation of the C-terminal Cdk site of PP1 (PP1ph) was examined by immunoblotting of EGFP traps from U2OS cells expressing EGFP-RepoMan-WT in Nocodazole-arrested (Mitosis) or non-synchronized (Nonsync) U2OS cells with a phospho-epitope specific antibody. (j) EGFP traps from non-synchronized HEK293T cells expressing EGFP-RepoMan-3A (RM 3A) were phosphorylated with Cdk2/Cyclin A. The unbound fractions were washed away before the addition of SDS sample buffer to the traps and immunoblotting for PP1 and PP1ph.