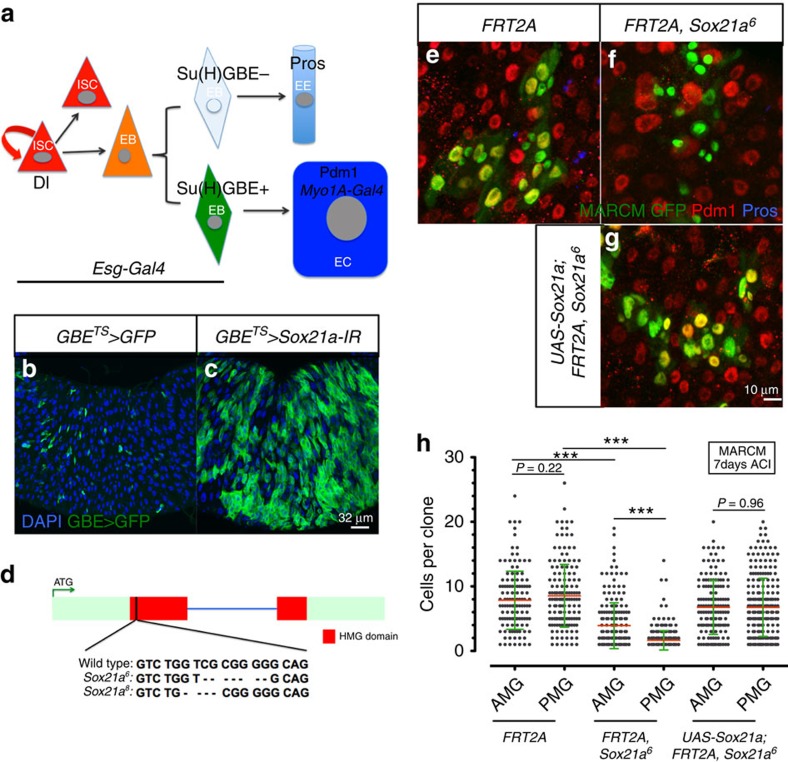
Figure 1. Sox21a is required for EB differentiation.
(a) Model of intestinal stem cell (ISC) lineages. The markers used in this study are Delta (Dl)-GFP/lacZ: ISC, escargot (esg)-Gal4 or Armadillo (Arm): progenitors (ISC+EB), Su(H)GBE-Gal4/lacZ: EB, Prospero (Pros): enteroendocrine cells (EE), Pdm1 or Myo1A-Gal4: enterocytes (EC). (b,c) Anterior midgut (AMG) of control fly and fly expressing a Sox21a-RNAi transgene in EBs for 14 days at 29 °C. Nuclei are stained for 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI; blue). EBs express GBE>GFP (green). (d) Schematic representation of Sox21a mutant alleles generated with CRISPR/Cas9 method. Sequences deleted are represented with dashed line. (e-g) Representative images of GFP-labelled MARCM clones from AMG of flies with indicated genotypes at 7 days after clone induction (ACI). Pdm1 (red) and Pros (blue). (h), Quantification of MARCM clone size for both AMG and posterior midgut (PMG) of experiments in e-g. Mean and s.e.m. are shown in h, with 136, 160, 221, 324, 166 and 274 clones (left to right) scored from 16 flies as a representative of three independent experiments. P values from Student's t-test (*P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001). One representative image from 16 midguts tested in one experiment, which was repeated three times, is shown in b,c and e-g.