Figure 1. Overview and validation of strategy to identify newly synthesized collagen by dermatan sulfate.
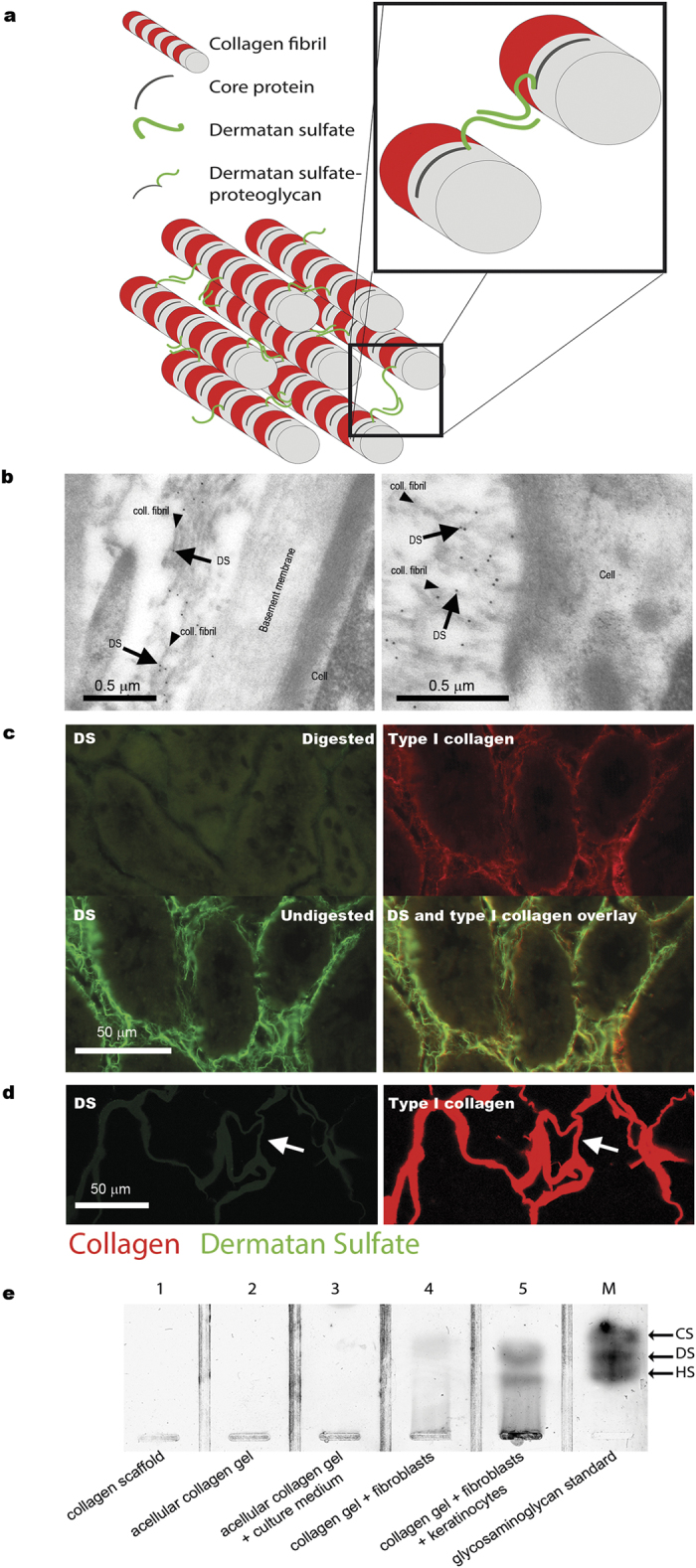
(a) Cartoon illustrating the intrinsic association of dermatan sulfate with collagen fibrils. (b) Identification of collagen fibrils using the anti-dermatan sulfate single chain antibody GD3A12. Arrows indicate immunogold labeling on collagen fibrils (rat kidney tissue, Bowman’s capsule), but not on other structures such as cells and basement membranes. (c) Specificity of the anti-dermatan sulfate antibody as evidenced by loss of immunostaining after digestion of dermatan sulfate by chondroitinase B (rat kidney tissue). Note co-localization of dermatan sulfate and type I collagen. (d,e) Absence of dermatan sulfate in pre-seeded/pre-implanted collagenous biomaterials as indicated by (d) immunostaining for dermatan sulfate (antibody GD3A12), (e) biochemical analysis of dermatan sulfate (agarose gel electrophoresis). In (d) arrows indicate identical areas stained for dermatan sulfate and type I collagen. In (e), lanes 1–3 represent acellular collagen gels/scaffolds, whereas lanes 4 and 5 represent cellularized gels. M, marker containing 5 ng each of chondroitin sulfate (CS), dermatan sulfate (DS) and heparan sulfate (HS). coll.fibril: collagen fibril.
