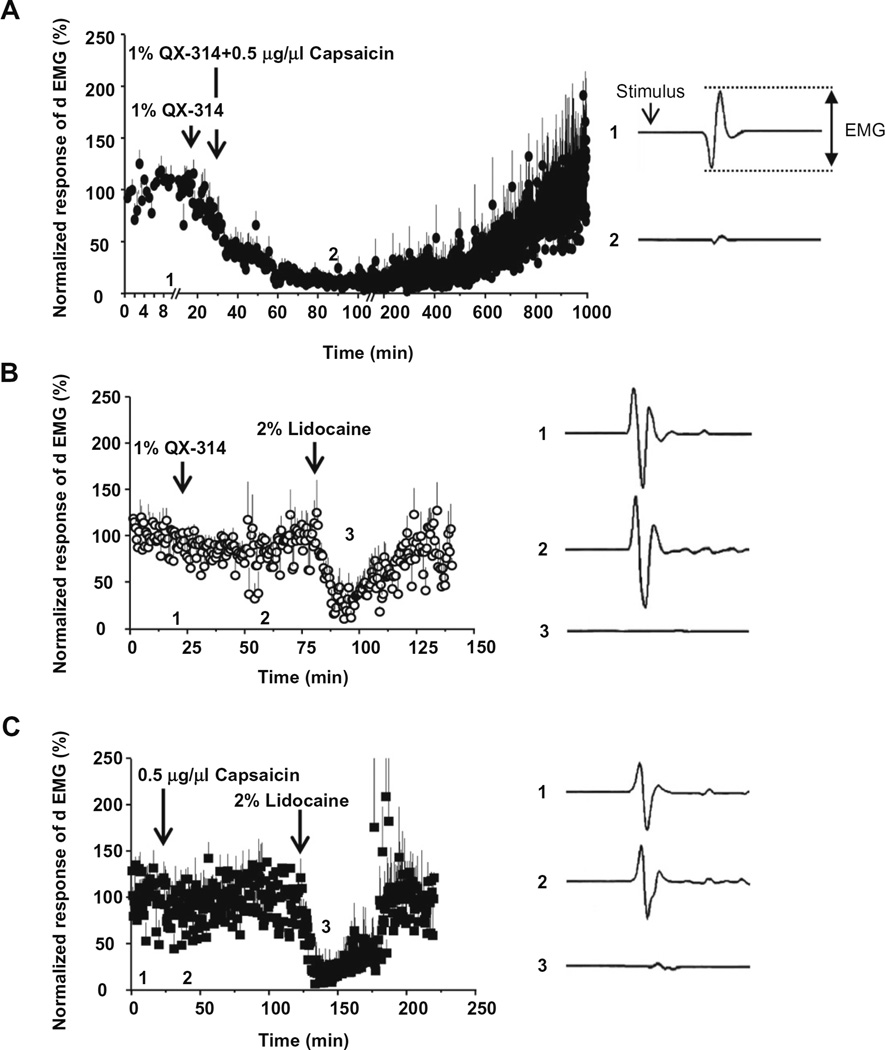
Fig. 7.
Effects of QX-314 and capsaicin applied onto sensory nerve tested with jaw-opening reflex. As a measure of jaw-opening reflex, the digastric muscle EMG (dEMG) in response to electrical stimulus (two and a half times to the threshold, ×2.5T) to anterior teeth was measured from the anterior digastric muscle. The drugs were applied onto inferior alveolar nerve. The data points plot normalized amplitudes of dEMG over time (Left panels in A–C). Right panels show dEMGs at the time points (before and after drug administration, respectively) indicated at each left panel. The normalized EMG decreased dramatically (by almost 99%) after the application of 1% QX-314 with 0.5 µg/µl capsaicin (A). However, application of 1% QX-314 or 0.5 µg/µl capsaicin alone produced only modest changes of dEMG amplitudes (approximately −13% in (B) and −20% in C). 2% lidocaine used as a positive control was applied at the end of the experiment.