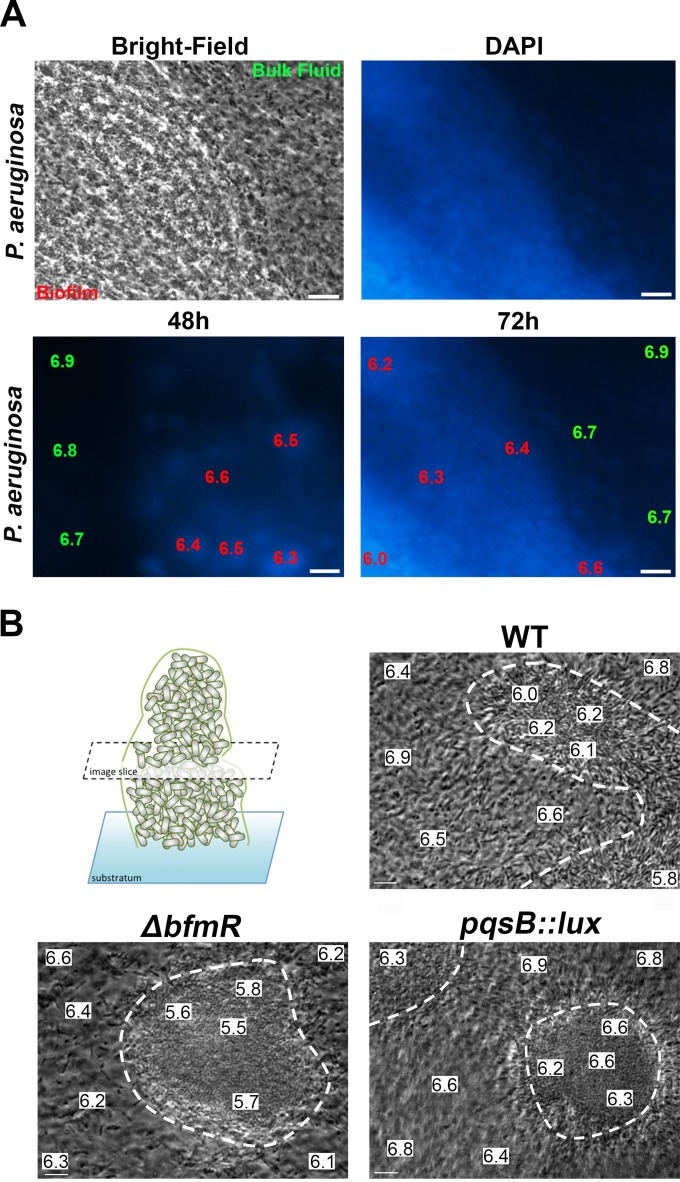
FIG 1.
Visualization of acidic microdomains in glass-adhered and flow chamber-cultivated Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. (A) Bright-field image (left) of DAPI-stained, glass-adhered biofilm (right). pH measurements were made using the ratiometric pH dye C-SNARF in P. aeruginosa wild-type biofilms that were costained with DAPI. Representative micrographs were captured at 48 and 72 h of biofilm cultivation. The data shown are the pH values in a 10-μm2 area of either the bulk fluid, the biofilm periphery, or biofilm interior. Scale bar, 10 μm. (B) Bright-field image slices of P. aeruginosa wild-type, ΔbfmR (eDNA overproducer), and pqsB::lux (eDNA underproducer) microcolonies after 6 days of flow chamber cultivation. pH measurements using C-SNARF in P. aeruginosa wild-type, ΔbfmR, and pqsB::lux microcolonies were determined in the bulk fluid, the biofilm-fluid interface, and biofilm core in the middle depth of the microcolony. The white dotted lines delineate the adhered microcolony edges. Representative micrographs are presented, and data are the pH values within a 10-μm2 area. Scale bar, 10 μm.