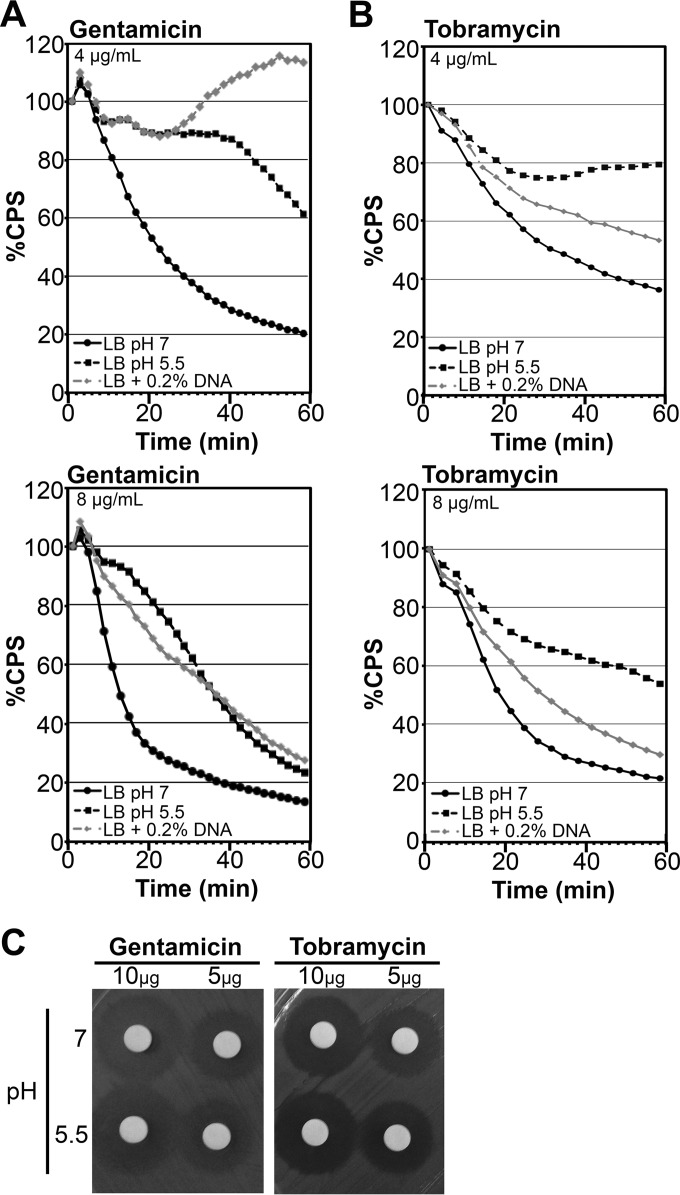
FIG 2.
Growth in the presence of extracellular DNA or under acidic conditions promotes aminoglycoside resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mid-log-phase PAO1::p16Slux cells were grown in LB, LB at pH 5.5, or LB plus 0.2% DNA, resuspended in LB (5 × 107 CFU), and treated with various concentrations of gentamicin (A) or tobramycin (B). Luminescence (CPS) was measured as an indication of viability in lux kill-curve experiments throughout 1 h of antibiotic exposure. Cells were resuspended in LB buffer alone as a negative control, and all data are expressed as percent survival relative to the untreated control. Values shown are the means for at least 3 replicates. The standard deviation was within ±10% of the mean. (C) Aminoglycoside antibiotics were resuspended in LB medium with a pH of 7 or 5.5 for 18 h and then spotted at 10 μg/disk or 5 μg/disk and applied to the aminoglycoside-sensitive Escherichia coli in a disk diffusion assay.