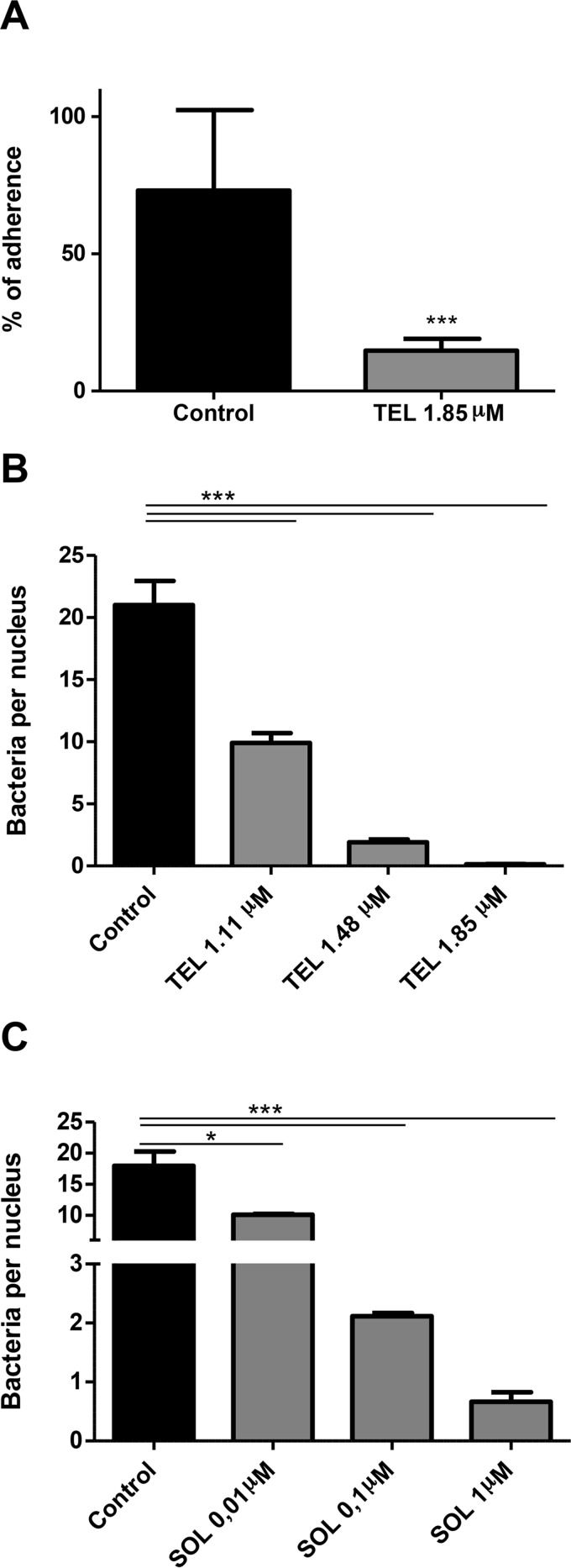
FIG 3.
Inhibition of bacterial adherence to Caco-2 cells in the presence of ketolides. Semiconfluent monolayers of Caco-2 cells were infected with E. coli O157:H7 ZAP198 at an MOI of 20 in the presence or the absence of telithromycin (TEL) or solithromycin (SOL), and the percentage of adherent bacteria (A) or the number of bacteria per nucleus (B and C) was determined as detailed in Materials and Methods. (A) Adherent bacteria were determined by counting the number of CFU that adhered to Caco-2 cells after incubation with medium alone (control) or medium supplemented with 1.85 μM telithromycin. Results are expressed as the mean percentage relative to the amount of seeded bacteria ± SEM. ***, P < 0.001, Student's t test. (B and C) Caco-2 cells were infected with ZAP198 in the presence of the indicated concentration of telithromycin (B) or solithromycin (C). The mean number of adherent bacteria per nucleus ± SEM was determined by fluorescence microscopy. The results of a representative experiment out of two that were performed are shown. Four slides per treatment and at least 24 fields per slide were counted. P < 0.0001, ANOVA; ***, P < 0.001, Newman-Keuls multiple-comparison test; *, P < 0.05, Newman-Keuls multiple-comparison test.