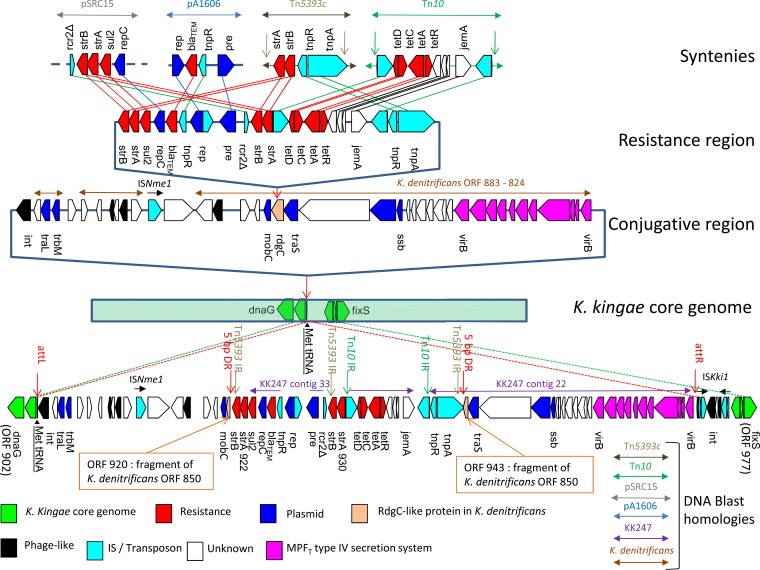
FIG 1.
Schematic representation of the putative genetic events that led to chromosomal insertion of the blaTEM gene in the K. kingae KWG1 genome and the genetic organization of the genomic region spanning bases 846108 to 926548. ORFs are represented by block arrows oriented according to the reading frame and color coded according to their putative functions or BLAST homologies. Green, K. kingae core genome (based on synteny with the K. kingae type strain ATCC 23330 genome); red, antimicrobial resistance; dark blue, plasmid transfer or replication; light salmon, RdgC-like protein in K. denitrificans strain ATCC 33394 (fragmented in KWG1); black, phage-like gene; light blue, IS or transposon (transposase, resolvase, and other); magenta, MPFT type IV secretion system; white, unknown function without homology or synteny with the K. kingae type strain genome. Transposons Tn10 and Tn5393c, as well as BLAST similarities to Salmonella enterica plasmid pSRC15, H. influenzae plasmid pA1606, K. kingae strain KK247, and K. denitrificans strain ATCC 33394, are indicated by colored horizontal double arrows. Syntenies with KWG1 are indicated by lines connecting ORFs with >50% identity on >80% of the shortest sequence. Isolated ISs (ISNme1 and ISKki1) are indicated by black horizontal arrows. Putative right and left att sites (attR and attL, respectively) and the 5-bp DR generated by insertion of the resistance region in the RgdC-like ORF are indicated by vertical red arrows. Tn5393c IRs (Tn5393 IR) and the 23-bp terminal IRs flanking Tn10 (Tn10 IR) are indicated by vertical green arrows.