Fig. 1.
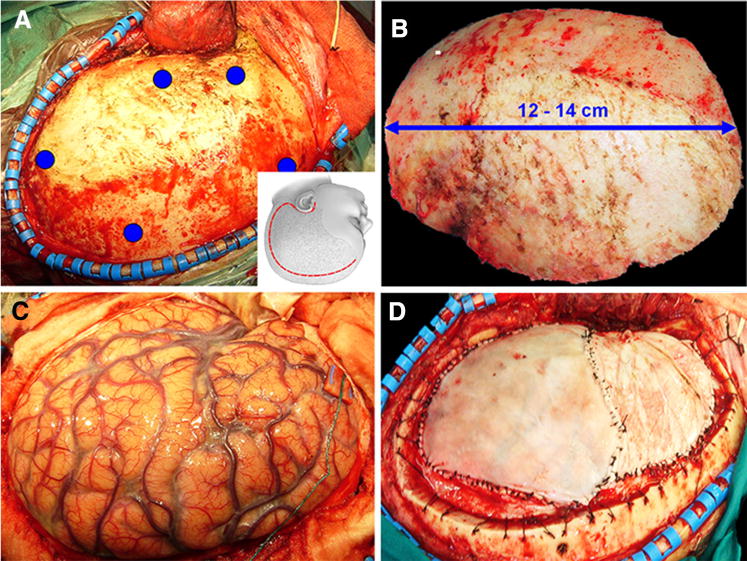
Intraoperative images of a decompressive craniectomy. a A curvilinear incision (inset, red line) is used to raise a large scalp flap and mobilize the temporalis muscle and fascia, thereby gaining a wide frontoparieto-temporal exposure; the positions of planned burr holes are indicated by blue dots. b The bone flap that is removed should measure 12–14 cm. c After opening the dura, the swollen brain herniates outward, relieving compression on medial structures and on the brainstem. d An augmentation duroplasty is performed to accommodate and protect the swollen brain. The inset in (a) is reproduced from: Operative Techniques in Neurosurgery, 7(1):10–15, 2004, with permission
