Figure 6.
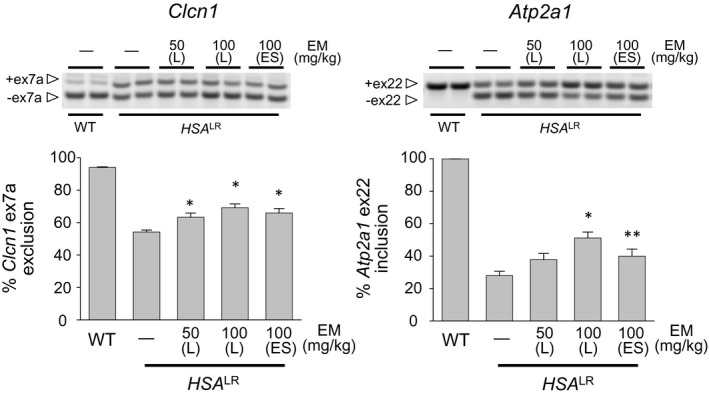
Oral administration (low‐dose, long‐term) of erythromycin improves splicing defects in Clcn1 and Atp2a1 in a DM1 mouse model. Analysis of Clcn1 (left) and Atp2a1 (right) alternative splicing by RT‐PCR in mice treated per oral with erythromycin (50 or 100 mg/kg for 21 days; n = 6 or more for experimental, control, and wild type). *P < 0.01. **P < 0.05. Error bars indicate SEM. DM1, myotonic dystrophy type 1; RT‐PCR, reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction; L; lactobionate, ES; ethylsuccinate.
