Figure 8. Model of H2O2‐induced modulation of presynaptic activity in spinal VH neurons .
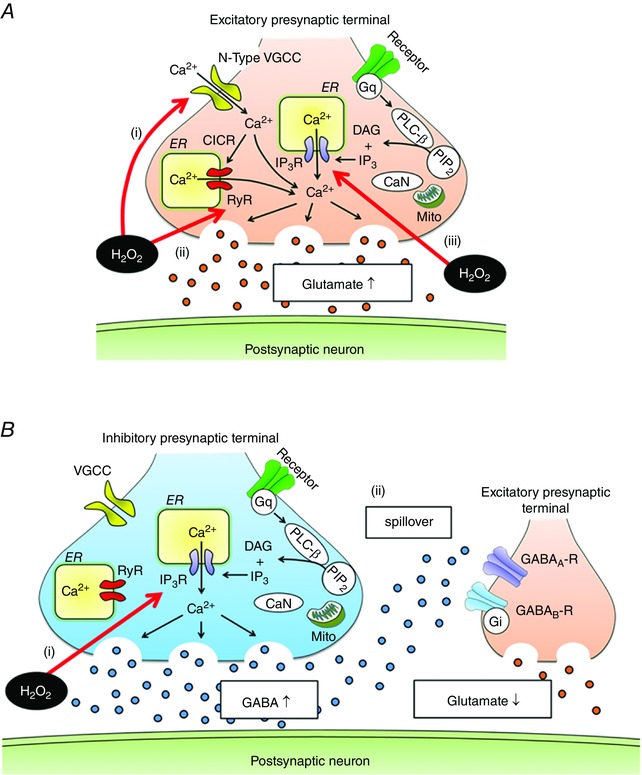
A, H2O2 stimulates glutamate release by Ca2+ influx via N‐type VGCC (i) and Ca2+ release from the ER via RyR (ii) and IP3R (iii). Oxidation of RyR cysteine residues increases RyR sensitivity to Ca2+, resulting in excessive activation of RyR‐mediated CICR. The effects of H2O2 on IP3R‐related signalling are downstream of PLC‐β. B, H2O2 increases GABAergic transmission by stimulating Ca2+ release from the ER via IP3R; its site of action is downstream of PLC‐β (i). Moreover, diffusion of GABA away from the release site activates presynaptic GABAA and to a lesser degree GABAB receptors (ii), thereby inhibiting glutamate release from excitatory presynaptic terminals. These effects by GABA may protect postsynaptic neurons from excitotoxicity resulting from excessive glutamate. Mito, mitochondria; CaN, calcineurin; PIP2, phosphatidylinositol 4,5‐bisphosphate; DAG, diacylglycerol.
