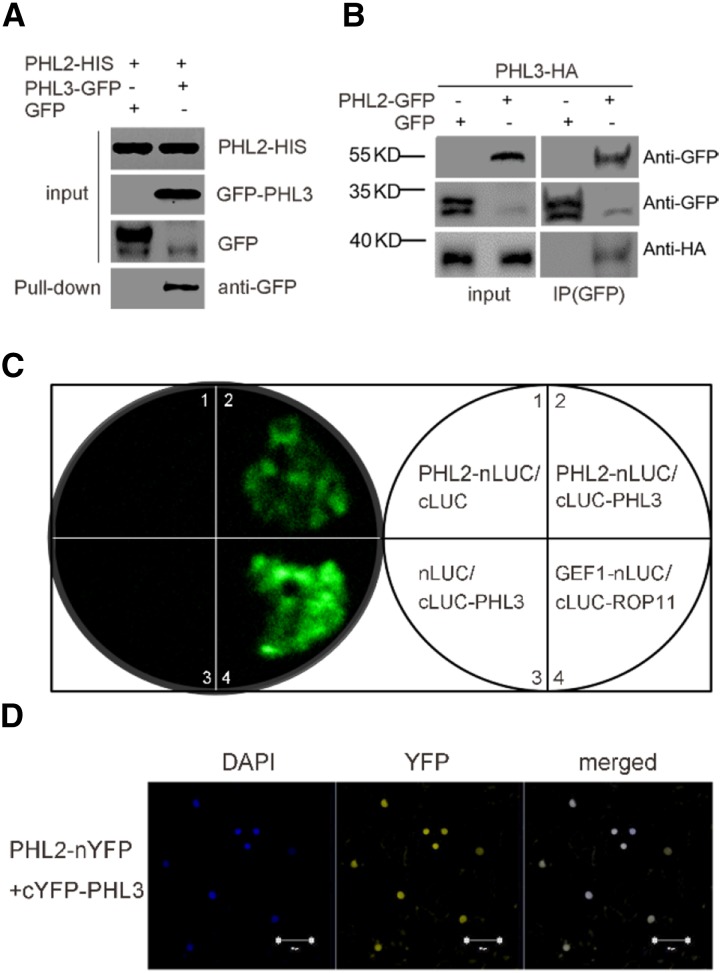
Figure 6.
PHL2 physically interacts with PHL3. A, Pull-down assay for the interaction of PHL2 and PHL3. PHL3-GFP or GFP was transiently expressed in the leaves of N. benthamiana. The expressed PHL3-GFP or GFP was pulled down by E. coli-produced PHL2-His proteins using anti-His antibodies. PHL3-GFP proteins in the pull-downed fraction were detected by immunoblot using anti-GFP antibody. B, Co-IP assay for the interaction between PHL2 and PHL3. Total proteins extracted from the leaves of N. benthamiana coexpressing 35S:PHL3-HA and 35S:PHL2-GFP or 35S:GFP were immunoprecipitated with anti-GFP antibodies. The PHL3-HA proteins in the precipitated fraction were detected by immunoblot using anti-HA antibody. C, LCI assays for the interaction of PHL2 and PHL3. The various pairs of the nLUC and cLUC constructs were coexpressed in the leaves of N. benthamiana, and LUC activity was observed 2 d after Agrobacterium tumefaciens infiltration. Two previously reported interacting proteins, GEF1 and ROP11, were used as the positive control (Li and Liu, 2012). D, BiFC assays for the interaction between PHL2 and PHL3. The constructs PHL2-nYFP and cYFP-PHL3 were coinfiltrated into the leaves of N. benthamiana. YFP fluorescence was detected 2 d after infiltration. The nuclei were revealed by DAPI staining. Bars = 50 μm.