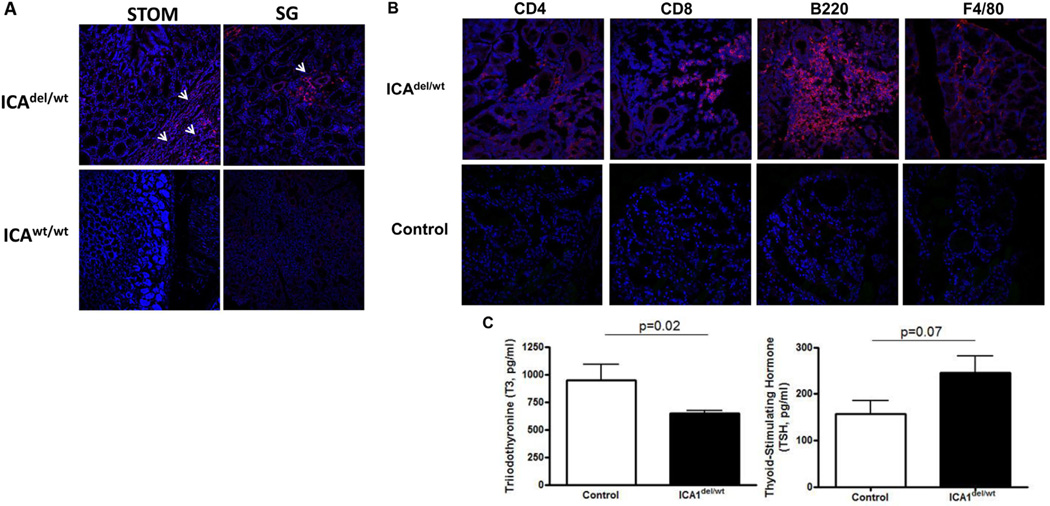
Fig. 4.
ICA69del/wt mice develop autoimmune thyroid disease. A. Immunohistochemistry showing lymphocytic infiltration into multiple tissues of 24-week old ICA69del/wt mice. Representative cryosections of stomach (STOM) and salivary glands (SG) were stained with anti-CD4 antibody (red). White arrows, infiltrating immune cells. B. Representative cryosections of thyroid glands of E14 immunized ICA69del/wt mice (16-weeks post immunization) were stained with anti-CD4, anti-CD8, anti-B220 and anti-F4/80 antibodies (red), showing the infiltration of CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells, B-cells and macrophages, respectively (upper panels). Age-matched wild type B6 mice immunized with E14 were used as controls (lower panels). C. Levels of thyroid hormones (total T3 and TSH) in sera of E14-immunized ICA69del/wt mice (filled bars, n = 9), in comparison to wild-type littermate controls (open bars, n = 8). Data were presented as mean ± SEM. p values of student t-test results were listed on top of each panel.