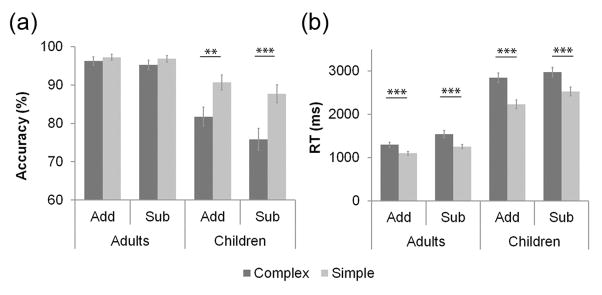
Figure 1. Performance during Addition and Subtraction problems in Adults and Children.
(a) Both Adults and Children were less accurate on Subtraction, compared to Addition, problems (p = .032). Adults were more accurate than Children (p < .001). While Adults were equally accurate in solving Complex and Simple problems (p = .228), Children were less accurate in solving Complex compared to Simple problems (p < .001). (b) Both Adults and Children were slower on Subtraction, compared to Addition, problems (p < .001). Adults were significantly faster than Children (p < .001). Both groups responded more slowly to Complex than Simple problems. The pattern was more pronounced in children than adults (p < .001). Add, addition. Sub, subtraction. *** p < .001. ** p < .01.