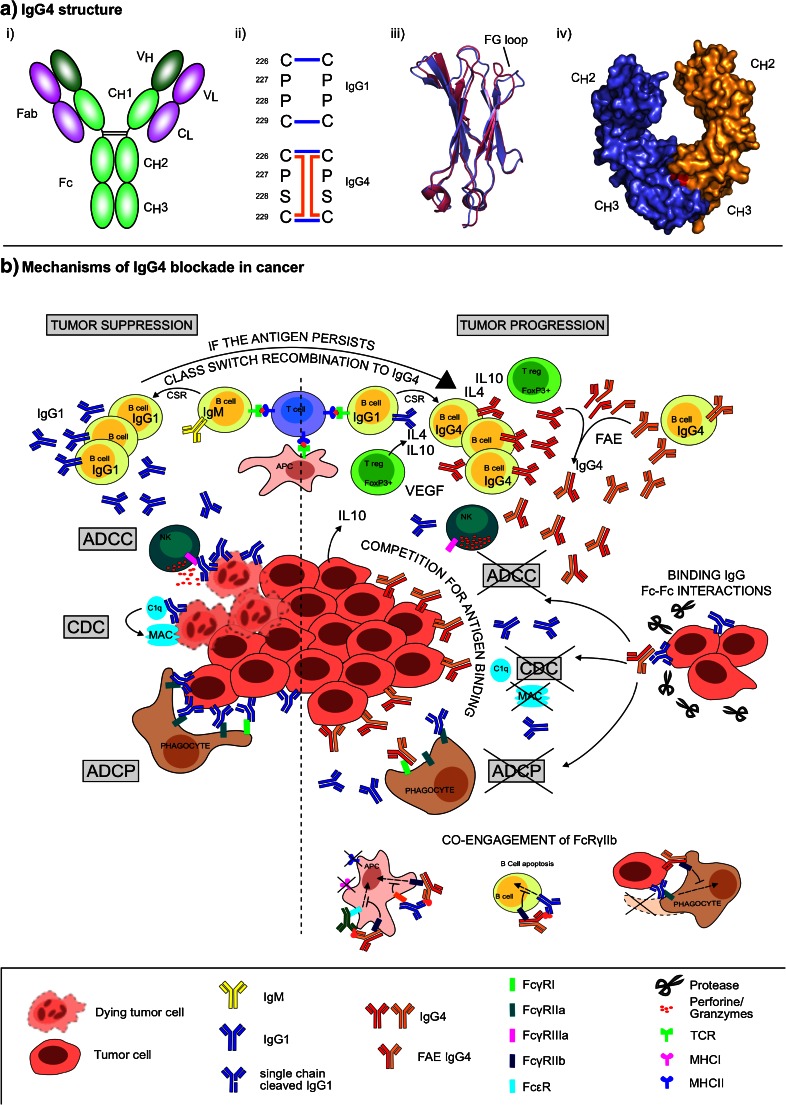
Fig. 1.
Structural and functional features of IgG4. a IgG4 structure: (i) IgG architecture. The Fab comprises VH, VL, CH1, and CL domains. The Fc region comprises CH2 and CH3 domains, and the hinge connects the Fab to the Fc. In IgG1, two disulfide bonds (black lines) covalently link the two heavy chains. (ii) The core hinge. In IgG1, residues 226–229 from the core hinge are CPPC. Inter-heavy chain disulfide bonds form between Cys226 and Cys229 (blue lines). Residues 226–229 are CPSC. In addition to the hinge disulfide bond pattern in IgG1, intra-heavy chain disulfide bonds can form between Cys226 and Cys229 (orange lines). (iii) Structure of the IgG CH2 domain. The IgG1 and IgG4 CH2 domains are colored in pink and blue, respectively. While the overall fold of the CH2 domains is similar, in IgG4, the CH2 domain FG loop adopts a unique conformation. (iv) Crystal structure of the IgG4-Fc region. The two heavy chains are colored in blue and orange. Arg409, positioned at the interface of the CH3-CH3 domain dimer, is colored in red. b Proposed mechanisms of IgG4 blockade in cancer. Tumor-associated humoral immunity could promote tumor suppression or progression (left and right of dotted line, respectively). Rapid production of anti-tumor IgG1 can eliminate antigen-expressing tumor cells through CDC, ADCC, and ADCP. Chronic antigen persistence along with a Th2-biased cytokine milieu (IL-4, IL-10, VEGF) expressed by resident Tregs and tumor cells can support sequential CSR of B cells to IgG4. IgG4 might thus be more affinity matured than clonally related IgG1 and may compete with IgG1 for binding tumor antigens. IgG4 could also undergo Fab-arm exchange with other IgG4s, resulting in functionally monovalent antibodies or antibodies with increased avidity. Inability of IgG4 to fix complement and to bind activating FcγRs on immune effector cells may result in blockade of antibody-mediated CDC, ADCC, and ADCP. Alternatively, binding of IgG4 to the inhibitory FcγRIIb with higher affinity than other IgG subclasses could form ICs together with other antibodies, such as IgG1, co-engaging FcγRIIb and activating FcγRs, dampening FcγR-mediated functions. Also, in the proteolytic conditions of tumor microenvironments (e.g., MMP), IgG1 bound to tumors could be cleaved on one heavy chain, causing partial dissociation and facilitating IgG4-Fc binding. This could interfere with IgG1-mediated effector functions or trigger intracellular uptake and clearance of the target from tumor cell surfaces