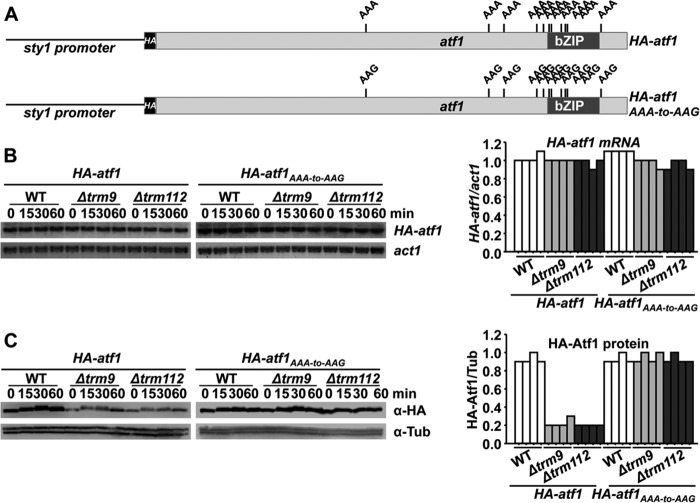
FIGURE 7.
Expression of a synthetic AAA-to-AAG atf1 gene renders wild-type Atf1 protein levels in cell lacking Trm9 or Trm112. A, schematic representation of HA-Atf1 and HA-Atf1AAA-to-AAG proteins, expressed from the constitutive sty1 promoter. The relative positions of the 11 AAA and AAG lysine codons are indicated. B and C, vectors carrying the wild-type (HA-atf1) or mutated atf1 genes (HA-atf1AAA-to-AAG) under the control of a constitutive promoter were integrated in the chromosomes of wild type and Δtrm9 and Δtrm112 strains. Rich media cultures of strains JF91 (sty1′::HA-atf1), JF94 (sty1′::HA-atf1AAA-to-AAG), PG136 (Δtrm9 sty1′::HA-atf1AAA-to-AAG), PG138 (Δtrm112 sty1′::HA-atf1AAA-to-AAG), PG139 (Δtrm9 sty1′::HA-atf1), and PG140 (Δtrm112 sty1′::HA-atf1) either untreated (0) or treated with 1 mm H2O2 for the indicated times were analyzed to determine HA-atf1 mRNA levels by Northern blot using an anti-HA probe (B) or HA-Atf1 protein levels by Western blot using monoclonal antibody against HA (C). The graphs on the right panels indicate the relative levels of HA-atf1/act1 mRNAs (B) or HA-Atf1/tubulin protein levels (C).