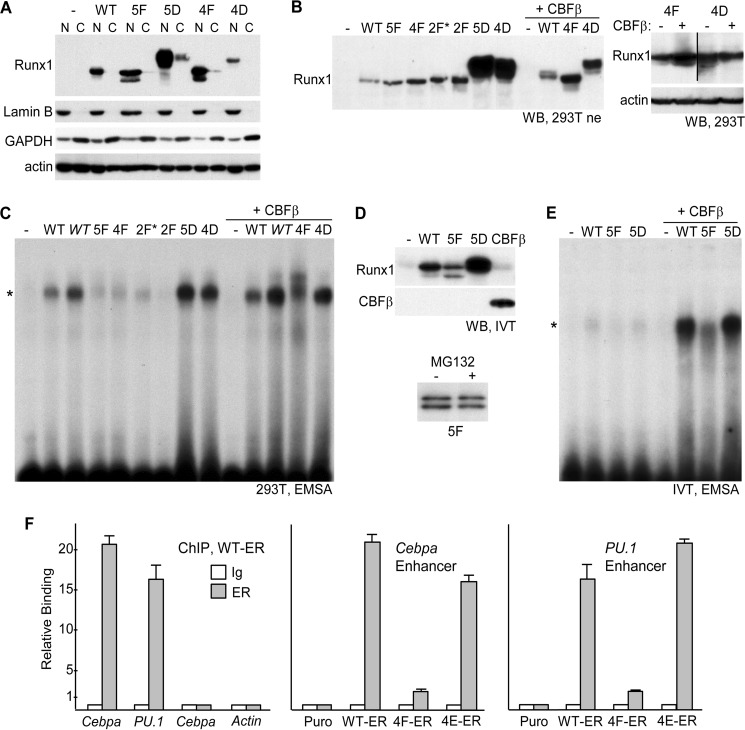
FIGURE 5.
A, 293T cells in 10-cm dishes were transfected with 6 μg of CMV (−) or CMV vectors expressing WT Runx1 or its 5F, 5D, 4F, or 4D variants. Nuclear (N) and cytoplasmic (C) extracts from equal cell numbers, prepared 48 h later, were subjected to Western blotting for Runx1, lamin B, GAPDH, or β-actin. B, 293T cells in 10-cm dishes were transfected with 6 μg of CMV (−) or CMV vectors expressing WT Runx1 or its 5F, 4F, 2F*, 2F, 5D, or 4D variants alone, or 3 μg of CMV or WT, 4F, or 4D with 3 μg of CMV-CBFβ. 20 μg of nuclear extracts prepared 48 h later were subjected to Western blotting (WB) using Runx1 antiserum (left). 293T cells in 6-well dishes were transfected with 1 μg of 4F or 4D, alone or with 1 μg of CBFβ, and total cellular proteins prepared 48 h later were subjected to Western blotting using Runx1 and β-actin antibodies (right). C, 6 μg of each nuclear extract were subjected to electrophoretic mobility shift analysis (EMSA) using a radiolabeled 32-bp double-stranded oligonucleotide containing a central consensus Runx1-binding site derived from the myeloperoxidase promoter. In addition, lanes with 12 μg of the WT or WT+CBFβ extracts (WT) were included. *indicates location of the specific gel shift band. D, Runx1 WT, 5F, or 5D, as well as CBFβ, were generated by in vitro transcription-translation (IVT) using 1 μg of linearized pcDNA3 expression vectors in a 50-μl reaction. Equal volumes, together with control reticulocyte lysate (−), were subjected to Western blotting for Runx1 and CBFβ (top). In addition, expression of 5F generated with or without 25 μm MG132 was analyzed similarly (bottom). E, after equalizing WT, 5F, and 5D protein based on densitometry, these samples as well as control lysate were analyzed for DNA binding by EMSA, alone or with addition of 7 μl of CBFβ lysate. F, 1E6 32Dcl3 Puro, WT-ER, 4F-ER, or 4E-ER cells cultured for 24 h in 4HT were subjected to ChIP assay using 2 μg of rabbit IgG or rabbit-anti-ERα (ER) antiserum followed by quantitative PCR using genomic primers specific for the +37-kb Cebpa enhancer, the −14 kb-PU.1 enhancer, the −2.5-kb Cebpa promoter region, or the β-actin promoter. Relative binding of WT-ER to each of these elements (left) or of WT-ER, 4F-ER, and 4E-ER to the Cebpa enhancer (center) or the PU.1 enhancer (right) is shown, with signal obtained with IgG in Puro cells set to 1.0 for each primer pair (mean and S.E. from three determinations).