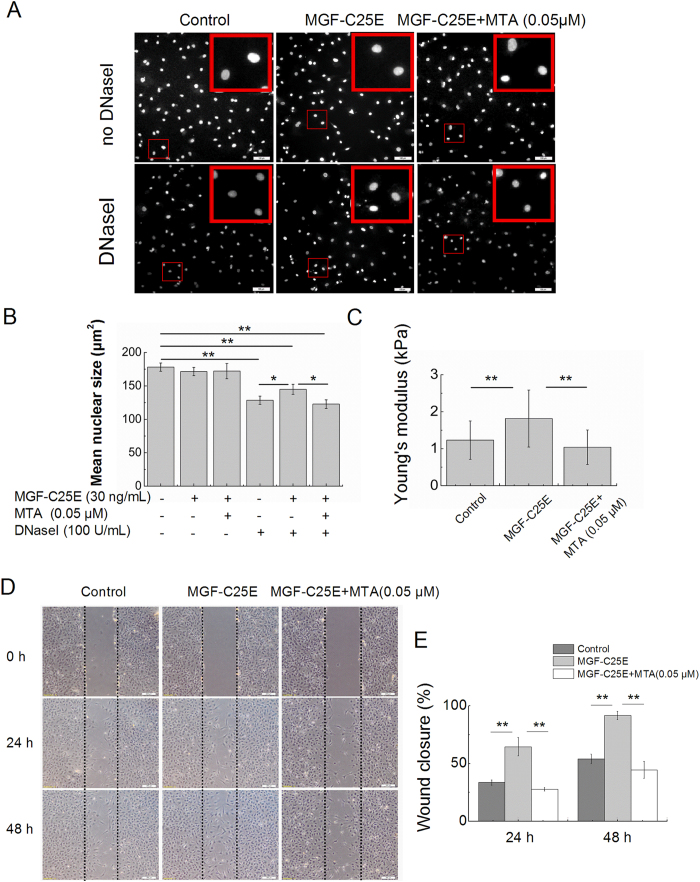
Figure 8. Effect of DNA methylation inhibitor (MTA) on MGF-C25E-induced chromatin condensation, nuclear stiffness and cell migration.
(A) In situ DNaseI-sensitivity assay. Tenocytes were exposed to MGF-C25E (30 ng/mL) in the absence or the presence of MTA (0.05 μM) for 24 h. DAPI-stained nuclei after 20 minutes of digestion with the 100 U/mL of DNaseI are shown. Bars = 100 μm. (B) Quantitative analysis of the mean size of nucleus after DNaseI exposure as shown in A. n = 3 in each group. (C) The nuclei of tenocytes exposed to MGF-C25E (30 ng/mL) show a higher Young’s modulus than those of the control cells, whereas pretreatment with MTA (0.05 μM) for 60 min inhibited the increase of Young’s modulus in tenocytes induced by MGF-C25E. n = 20 in each group. (D) Images of the migration of tenocytes treated with MTA, as evaluated through a scratch wound assay. Bars = 200 μm. The migration was evaluated by determining the ratio of the residual wound area to the initial wound area. n = 3 in each group. Data are expressed as the means ± SD; *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01.