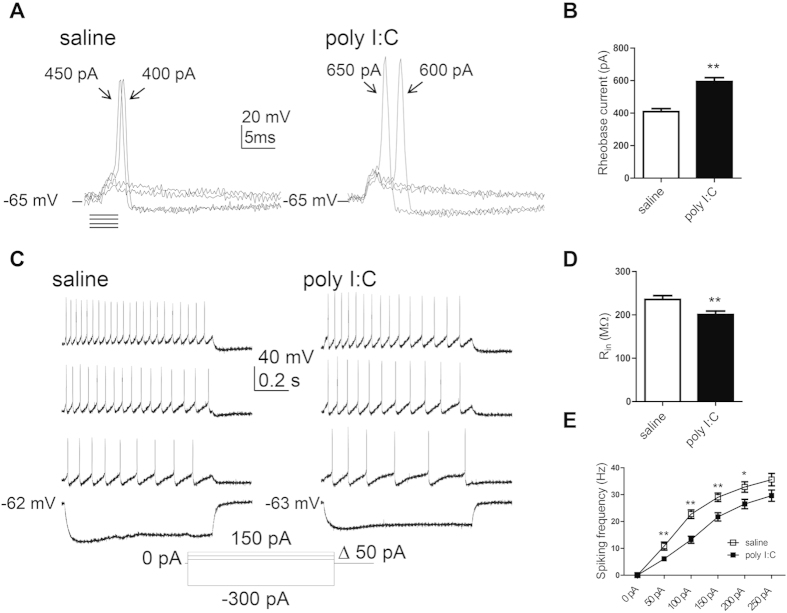
Figure 1. Cultured hippocampal neurons from offspring of polyI:C-injected mothers exhibit lower intrinsic excitability properties.
(A) Representative superimposed traces of single action potentials from cultured hippocampal neurons from offspring of saline (left panel) and polyI:C (right panel) -injected mothers. Solitary spike was evoked by 2 ms squared pulse injection of current steps starting from 200 pA in 50 pA increments, in the presence of glutamate and GABAA ionotropic receptors blockers (10 μM NBQX, 10 μM AP-5, 30 μM picrotoxin and 10 μM bicuculline methyl iodide). The line represents the starting resting potential before current injection. (B) Significantly higher current injection was required to evoke a single spike in cultured hippocampal neurons from offspring of polyI:C-injected mothers compared to those from offspring of saline-injected mothers (594 ± 25 pA, n = 54 from 6 poly I:C-injected mothers versus 409 ± 19 pA, n = 44 from 6 saline-injected mothers, t(96) = 5.69, p < 0.0001). (C) Representative traces of evoked spiking activity of cultured hippocampal neurons from offspring of saline (left panel) and polyI:C (right panel) -injected mothers. Spiking activity was evoked by 800 ms squared pulse injection of series of current steps starting from −300 pA up to 250 pA in 50 pA increments, in the presence of the glutamate and GABAA ionotropic receptors blockers. (D) Cultured hippocampal neurons from offspring of polyI:C-injected mothers exhibited significantly lower membrane input resistance compared to those of saline-injected mothers (Rin = 200 ± 8 MΩ, n = 56 from 6 polyI:C-injected mothers versus Rin = 236 ± 9 MΩ, n = 41 from 6 saline-injected mothers; t(95) = −2.79, p < 0.01). (E) frequency-current plots showing that the firing frequency in cultured hippocampal neurons from offspring of polyI:C-injected mothers is lower compared to that from offspring of saline-injected mothers. Repeated ANOVA yielded main effects of current injection, prenatal treatment and significant interaction between current injection and prenatal treatment (F(5, 450) = 235.2, p < 0.0001; F(1, 90) = 11.81, p < 0.001 and F(5, 450) = 3.7, P < 0.003 respectively; post hoc p’s < 0.05; n = 55 from 6 polyI:C-injected mothers versus n = 37 from offspring of 6 saline-injected mothers).