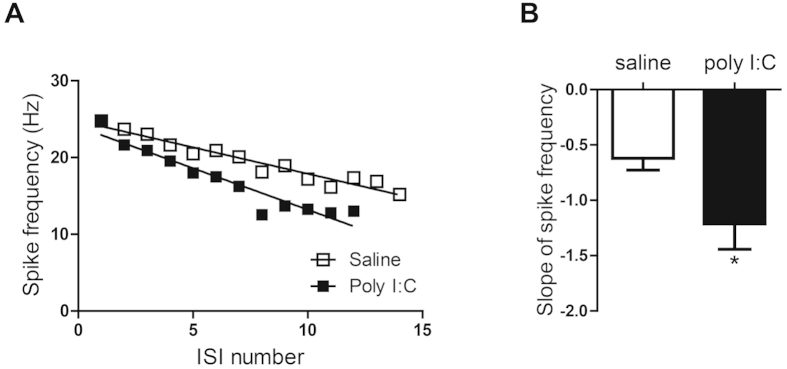
Figure 2. Cultured hippocampal neurons from offspring of polyI:C-injected mothers exhibit stronger spike frequency adaptation.
(A) Representative frequency-interspike interval (ISI) plot showing the stronger spike frequency adaptation as calculated by the slope of the linear regression of the spike frequency as a function of the ISI number. (B) Hippocampal neurons from offspring of polyI:C-injected mothers exhibit a larger slope (S) of spike frequency adaptation than those from offspring of saline-injected moms (S = −1.21 ± 0.22, n = 35 from 6 polyI:C-injected mothers versus S = −0.62 ± 0.11, n = 38 from 6 saline-injected mothers; t(71) = −2.25, p < 0.05).