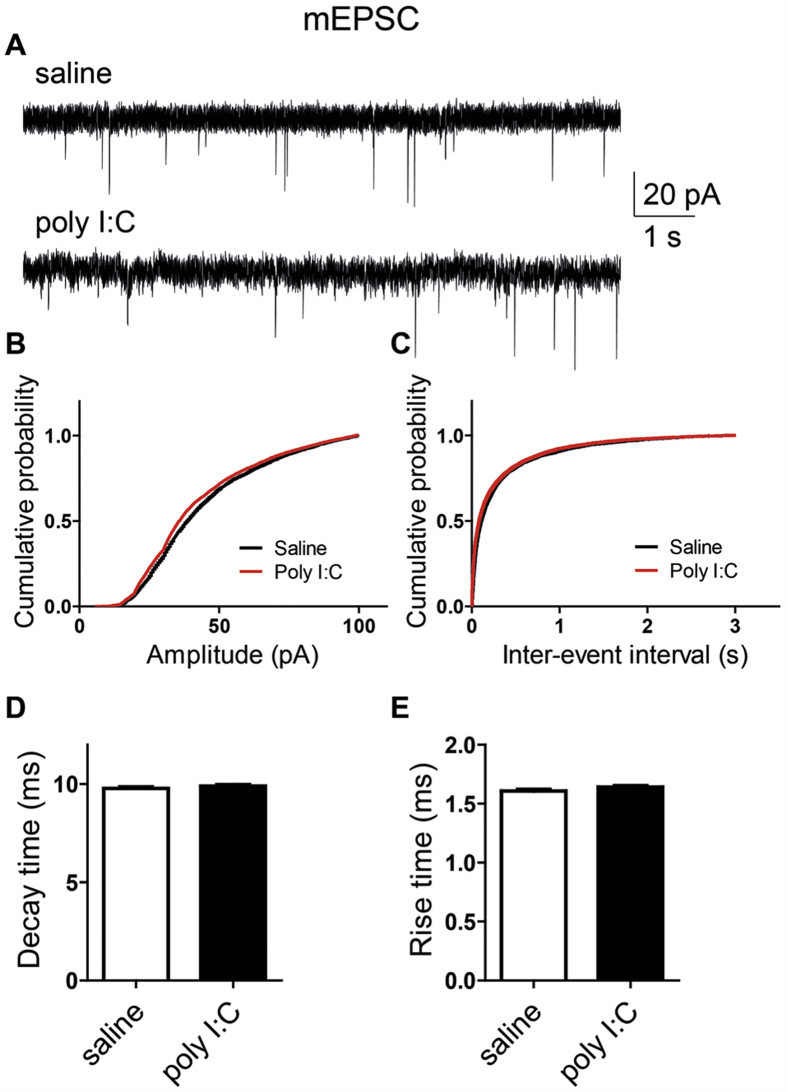
Figure 6. Cultured hippocampal neurons from offspring of saline and polyI:C-treated mothers exhibit similar mEPSC properties.
(A) Representative voltage-clamp recording of mEPSCs in cultured hippocampal neurons from offspring of saline (top) and polyI:C (bottom)-injected mothers. (B) Cumulative probability-amplitude plots show no differences in the mEPSC amplitude of cultured hippocampal neurons from offspring of saline and polyI:C-injected mothers (n = 35 cells and n = 40 cells, respectively, in each group from 6 different mothers). (C) Cumulative probability-interevent interval plots show no differences in the mEPSC frequency of cultured hippocampal neurons from offspring of saline and polyI:C-injected mothers (n = 32 cells and n = 37 cells, respectively, in each group from 6 different mothers). (D) No differences were found in the mEPSC decay time in cultured hippocampal neurons from offspring of saline and polyI:C-injected mothers (n = 35 cells and n = 40 cells, respectively, in each group from 6 different mothers). (E) No differences were found in the mEPSC rise time in cultured hippocampal neurons from offspring of saline and polyI:C-injected mothers (n = 35 cells and n = 40 cells, respectively, in each group from 6 different mothers). For each recorded neuron, 200 events were analyzed.